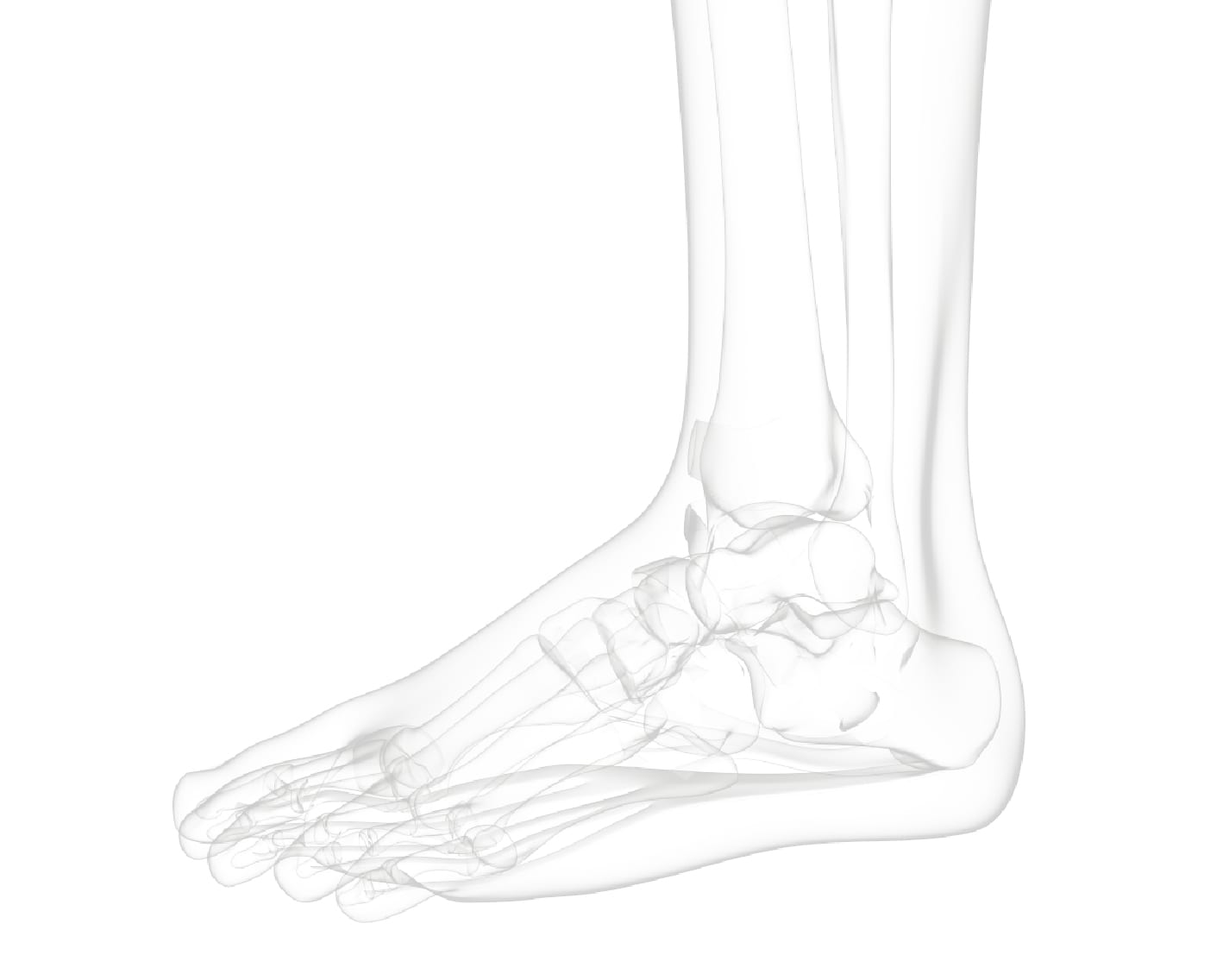
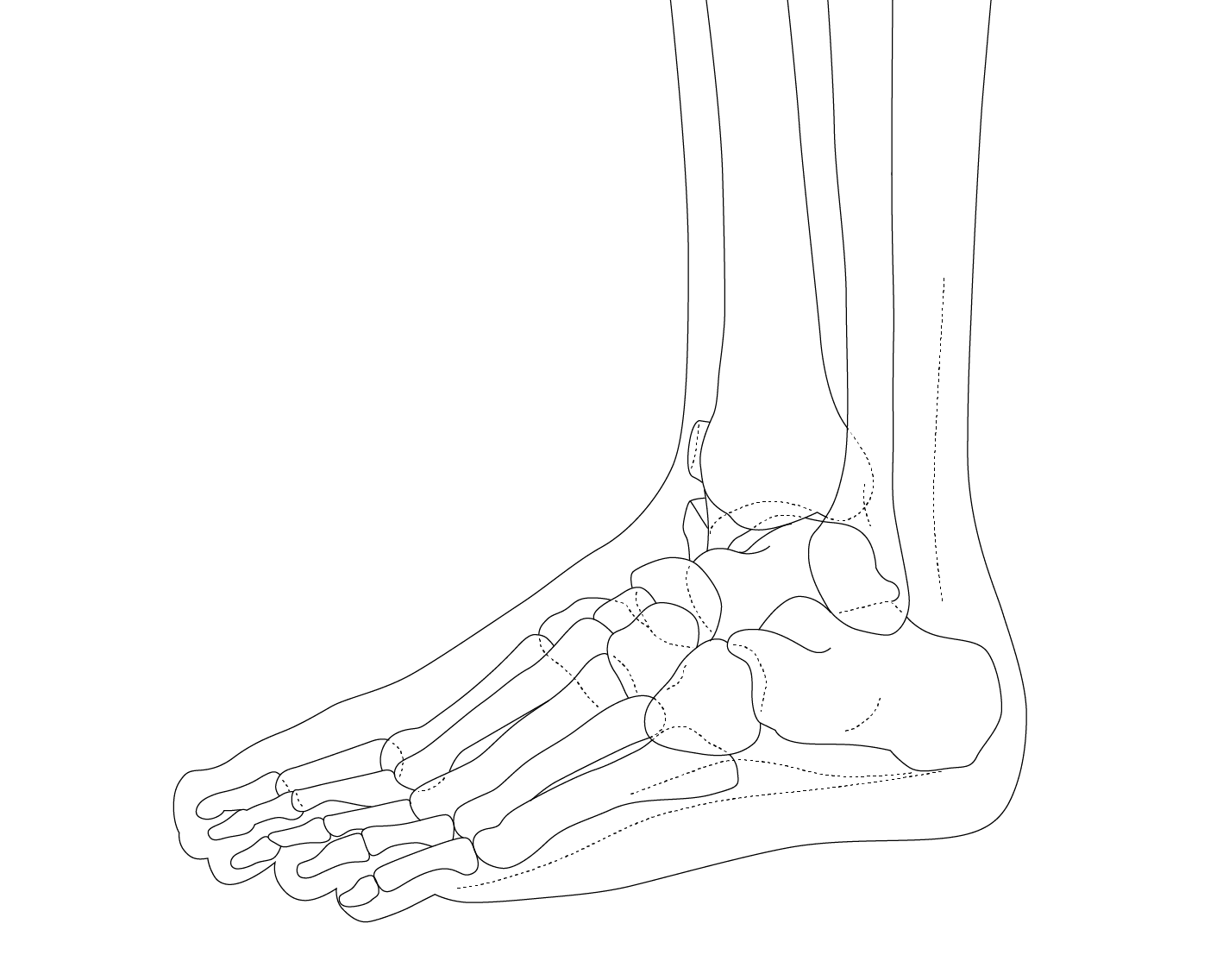
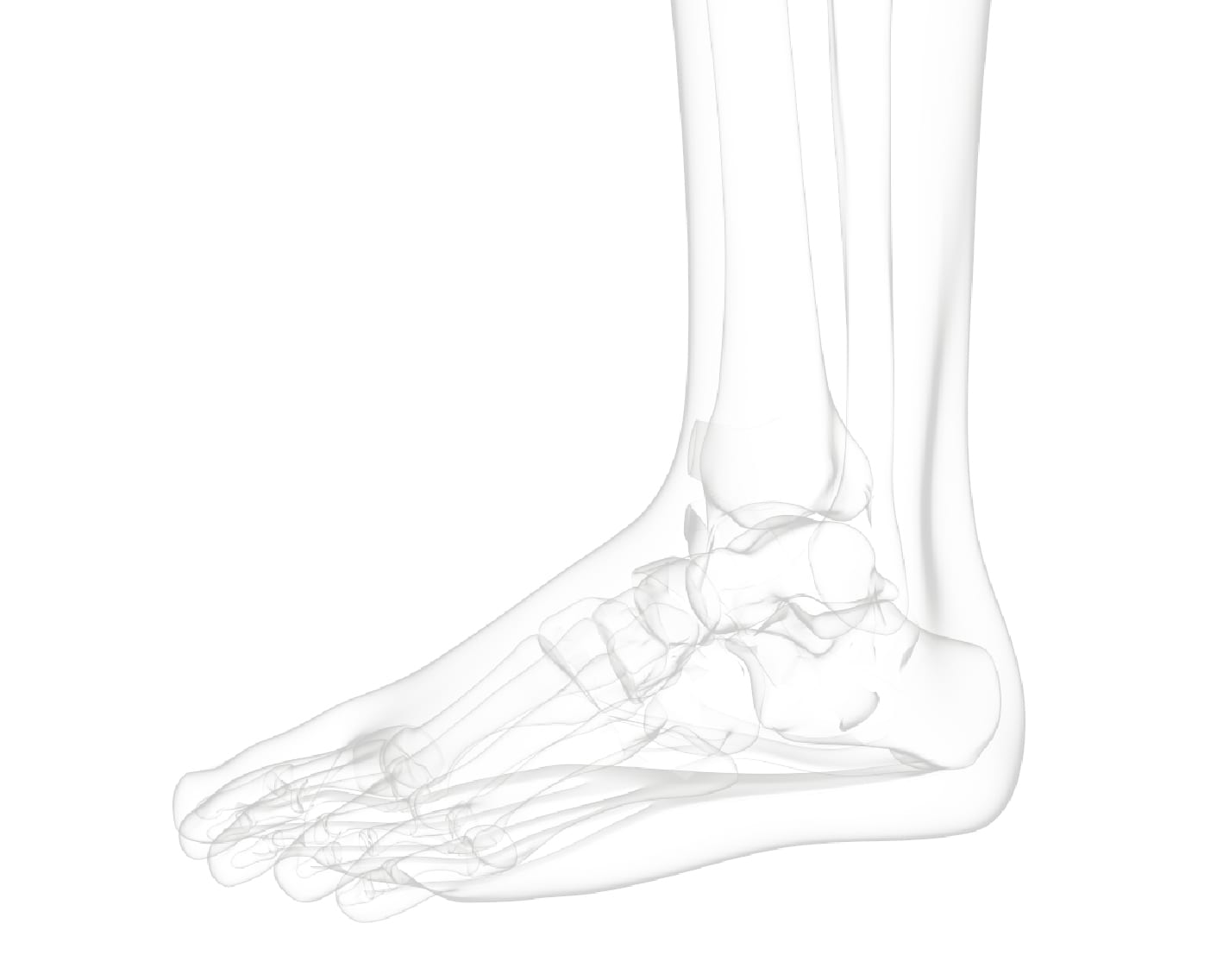
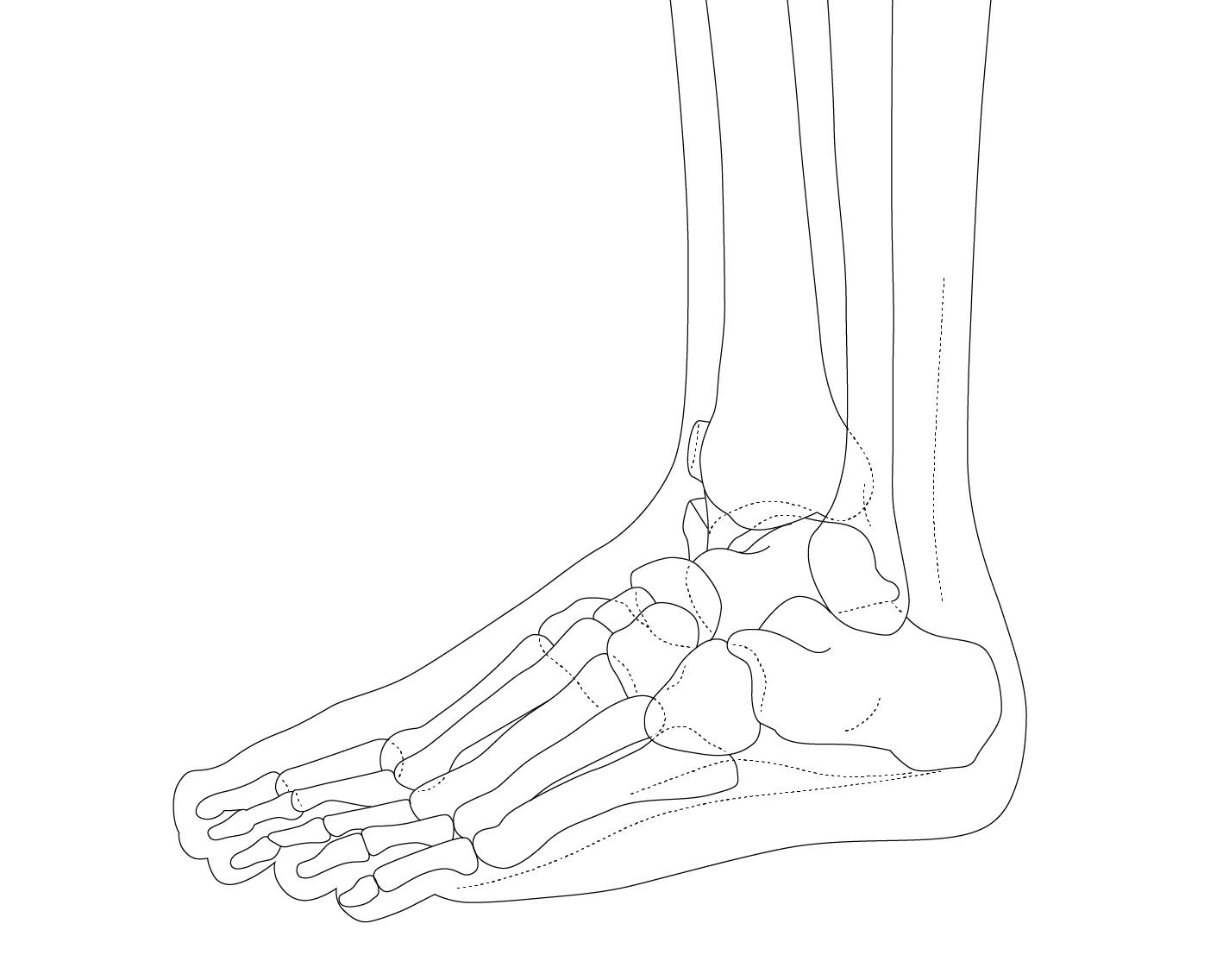
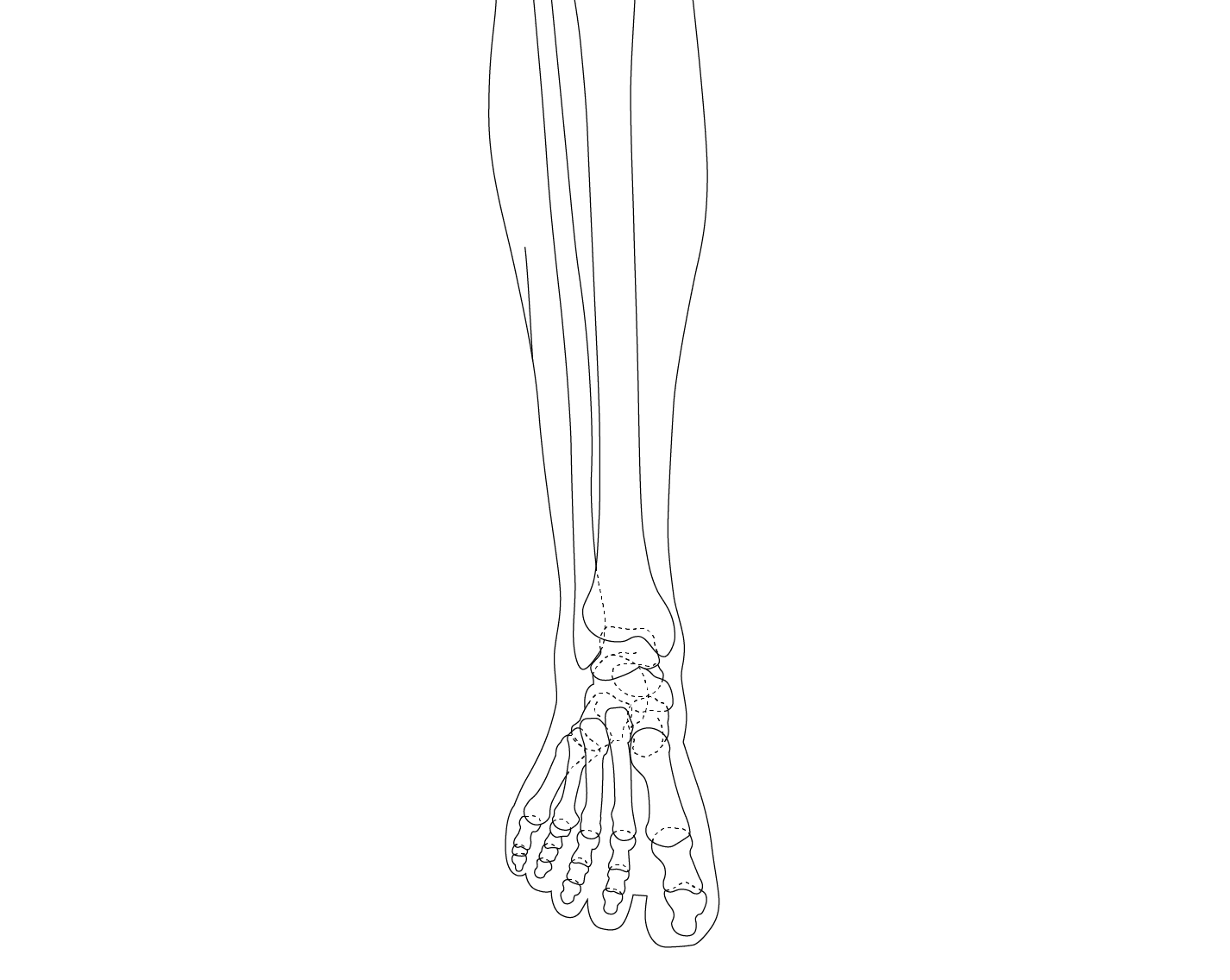
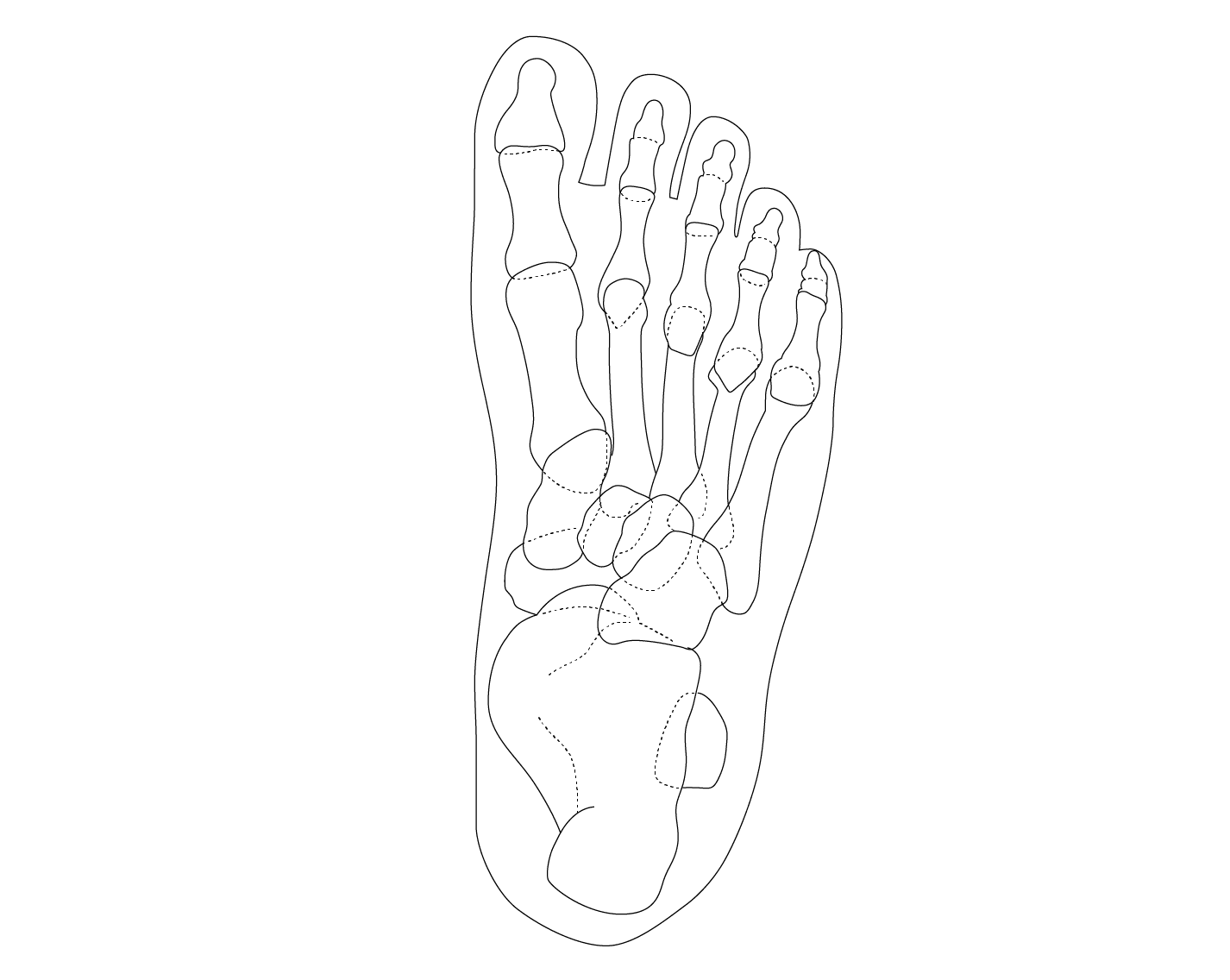
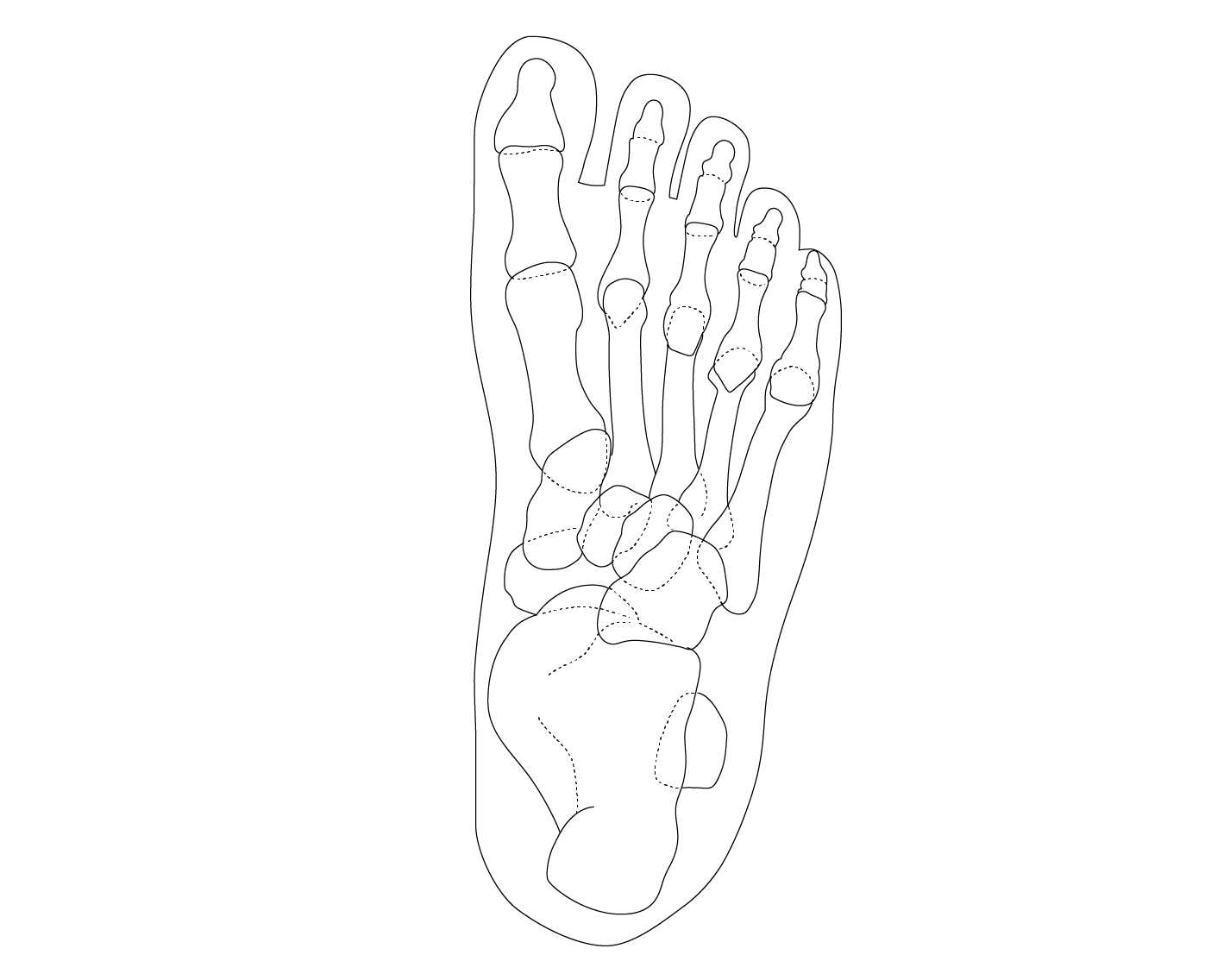
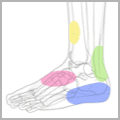
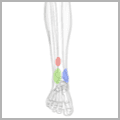
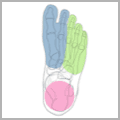
The ankle is one of the most resilient joints in the body composed of three bones, the tibia (shin bone), fibula (thinner bone on the outside of the ankle), and the talus (the foot bone that sits above the heel bone). It is a combination of a hinge joint and a gliding joint and is unique in that it gets wider and more stable with the ankle flexed up in dorsiflexion. This is why most sprains occur with the ankle flexed down, in plantarflexion. The joint capsule holds the bones together and is lined by a synovial membrane with makes the lubricating joint fluid. The ligaments are dense bands of fibrous tissue that help the joint capsule hold the bones together along the lines of stress. The articular cartilage provides the smooth gliding surface and cushion between the bones. When the cartilage gets damaged, arthritis results.
Amazingly, the cartilage in the ankle joint is much tougher than the cartilage of the knee. Arthritis is nine times less common in the ankle than in the knee and is usually a result of prior trauma, than primary osteoarthritis, even though the cartilage layer is much thinner than the knee. This is not well understood. Especially since the ankle transmits up to two times the force (bodyweight) of the knee with only 1/3 the surface area.
Traumatic injuries to the foot and ankle occur frequently in athletes. The articulation between the tibia and the talus support 90% of body weight, with the articulations between the fibula and the tibia, and the fibula and the talus conferring stability. A high ankle sprain, when the syndesmotic ligament is torn, disrupts the ligament between the two leg bones, the tibia and fibula and usually requires surgery as this injury is highly unstable. Ankle injuries most commonly occur with twisting and inversion (rolling in) forces resulting in ankles sprains and/or fractures (broken bones).
Overuse injuries to the foot and ankle are also quite common in athletes . The repetitive forces applied to the foot and ankle during running often lead to inflammation and tendonitis of the foot and ankle. These syndromes include Achilles tendonitis, peroneal tendonitis , posterior tibial tendonitis and plantar fasciitis. With additional activity , stress fractures of the calcaneus(heel), and metatarsals (foot bones) may occur.