Thumb Fractures Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
A thumb fracture occurs when one of the bones in the thumb breaks, often from a fall, a direct blow, or a sports injury. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and trouble gripping or holding objects. Prompt diagnosis and proper treatment are important to restore movement and strength and prevent long-term joint stiffness.
Start with our quick Symptom Assessment or connect directly with an Upswing Coach today.
Request an AppointmentReady to take the next step?
Start your symptom assessment or connect with a coach instantly.
Find Relief TodayOverview
The thumb plays an important role in grasping objects, so a thumb fracture can significantly affect your ability to pick up and hold items.
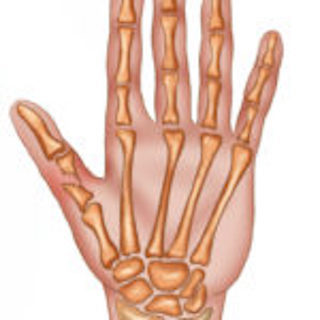
Your thumb is made up of two bones, called phalanges. These small bones connect to a larger bone in your hand, known as the first metacarpal.
The most common thumb fractures involve the base of the first metacarpal and the area where your thumb attaches to the wrist, referred to as the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint.
Two specific types of fractures that affect the CMC joint are:
- Bennett fracture: A clean break at the base of the thumb involving the joint.
- Rolando fracture: Occurs when the bone is shattered in the same location.
What causes Thumb Fractures?
Thumb fractures are most common in these sports:
Thumb fractures usually result from trauma or sudden force applied to the thumb. Common causes include falls, sports injuries, or accidents where the thumb is bent backward or struck directly. In some cases, fractures can also occur from twisting motions or strong muscle contractions during intense physical activity.
- How the Injury Occurs: A thumb fracture often happens when the thumb is forcefully bent, twisted, or compressed. This may occur from falling onto an outstretched hand, being struck by an object, or colliding with another person. The sudden stress on the joint or bone exceeds its strength, causing a break or crack.
- Common Everyday Causes: Thumb fractures are not limited to athletes. They can also occur in everyday situations, such as:
- Falls at home or work, where someone lands awkwardly on their hand.
- Accidents involving tools or machinery that crush or jam the thumb.
- Car or bike accidents, where the thumb absorbs direct impact.
- Repetitive strain during manual labor, like construction or assembly work, can place continuous stress on the thumb joint.
These non-sport injuries can be as painful and may require similar care and recovery time.
Thumb fractures are most common in the following sports:
- Baseball: The thumb can jam or hyperextend while catching or hitting the ball.
- Softball: A fast-moving ball or an awkward bat grip can put sudden pressure on the thumb joint.
- Basketball: The thumb may bend backward if the ball hits the hand unexpectedly during a pass or rebound.
- Football: Direct impacts or falls during tackles can forcefully bend or twist the thumb.
- Hockey: Contact with sticks, pucks, or collisions can stress the joint and cause fractures.
- Wrestling: Strong grips and twisting during holds or takedowns can injure the thumb.
- Skiing: Known as “skier’s thumb,” it occurs when the thumb gets caught in a ski pole strap during a fall.
- Volleyball: Forceful ball impacts or blocking at the net can cause sudden thumb hyperextension.
Symptoms
A broken thumb will cause immediate pain and limit your ability to grip or move your hand. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Intense pain and swelling at the base of the thumb: Soon after the injury, the area may become sore, swollen, and tender.
- Restricted or no mobility in the thumb: Bending, straightening, or moving the thumb may be difficult or impossible.
- Noticeable deformity of the thumb: The thumb may appear crooked, shortened, or misaligned.
- Extreme tenderness over the thumb: Even light pressure can cause significant discomfort.
- Visible bump or misalignment: The fractured bone may sometimes create a noticeable protrusion.
- Numbness or coldness: This may indicate nerve or blood vessel involvement.
Because thumb fracture symptoms can closely resemble a severe sprain, it is essential to see a doctor promptly for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
When to see a doctor
See a doctor as soon as possible if you experience severe pain or swelling after an injury and suspect a thumb fracture. Delaying treatment can worsen the injury and slow recovery.
During your appointment, the doctor will examine your thumb and will order X-rays to confirm a fracture and rule out other causes of pain, such as a sprain.
Non-operative treatment
If the bone fragments are not displaced, meaning they haven’t shifted significantly, or if the fracture does not involve a joint, your doctor may treat the thumb without surgery.
Non-surgical treatment typically involves wearing a specially designed cast called a thumb spica cast for 4 to 6 weeks. Routine X-rays may be taken during this period to ensure the bones remain properly aligned as they heal.
Try these exercises to help your condition:
Below is a PDF of the exercise program.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be necessary to treat a thumb fracture when the bones are misaligned, unstable, or involve a joint surface. It’s typically recommended if:
- The bones are displaced: The broken ends of the bone have moved out of position and need realignment.
- The fracture involves a joint: Damage extending into the thumb joint can affect long-term movement and stability if not repaired properly.
- You have a Rolando or Bennett fracture: These are complex fractures near the base of the thumb that often require surgical correction for proper healing.
During surgery, your surgeon will carefully realign the bone fragments and use pins, plates, or screws to hold them securely in place.
Two main techniques may be used:
- Internal fixation: small screws or plates are placed inside the thumb to stabilize the fracture.
- External fixation: pins are inserted into the bone and connected to a device outside the body to keep the thumb steady during healing.
These surgical methods help restore thumb alignment, promote healing, and preserve joint motion for long-term hand function.
After surgery, immobilization with a splint or cast is often necessary to protect the repair and allow proper bone healing before movement exercises begin.
Recovery
Recovery from a broken thumb varies depending on the severity of your injury and whether or not you need surgical treatment.
For non-operative treatment, you should expect to wear a spica cast for 4 to 6 weeks.
If you’ve had surgery, you must wear a cast or splint for about 6 weeks afterward. By the time your cast is ready to come off, your doctor will have removed any stabilizing pins. However, if you’ve had a plate or screws placed, they will remain.
With proper treatment, most thumb fractures have good outcomes. However, it can take three months or longer to regain full use of your hand. You can return to your sport when you have a full range of motion, strength with no pain, and clearance from your doctor.
Dr. Jay Kimmel is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine, arthroscopic surgery, and shoulder and knee disorders. He completed his orthopedic training at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center and a Sports Medicine Fellowship at Temple University.
Dr. Kimmel previously served as the Director of the Connecticut Sports Medicine Institute at Saint Francis Hospital and has held faculty appointments as Clinical Assistant Professor in the Departments of Orthopedics and Family Medicine at the University of Connecticut. He has extensive experience caring for athletes as a team physician for high school and collegiate programs and continues to teach in the athletic training departments at Westfield State University and Springfield College.
Find the Support You Need — Right When You Need It
Whether you’re managing pain for the first time, need ongoing guidance, or require expert medical care, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
ORTHO DIRECT
Video visit with an orthopedic doctor for advice and a care plan.
$30
/MonthMRI DIRECT
Fast, affordable MRI with orthopedic review. No insurance required.
$499
/MonthFrequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for a broken thumb to heal?
Recovery usually takes 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the fracture type and treatment method. With physical therapy, full function often returns soon after.
Will I be able to use my hand normally again?
Absolutely. With early diagnosis, proper care, and guided exercises, most patients regain full hand and thumb function.
Is surgery always required for a thumb fracture?
No, many thumb fractures heal well with casting or splinting alone. Surgery is only needed for complex or displaced fractures.
Can I prevent thumb fractures in the future?
Yes, wearing protective gear during sports, strengthening hand muscles, and practicing safe techniques can significantly reduce risk.