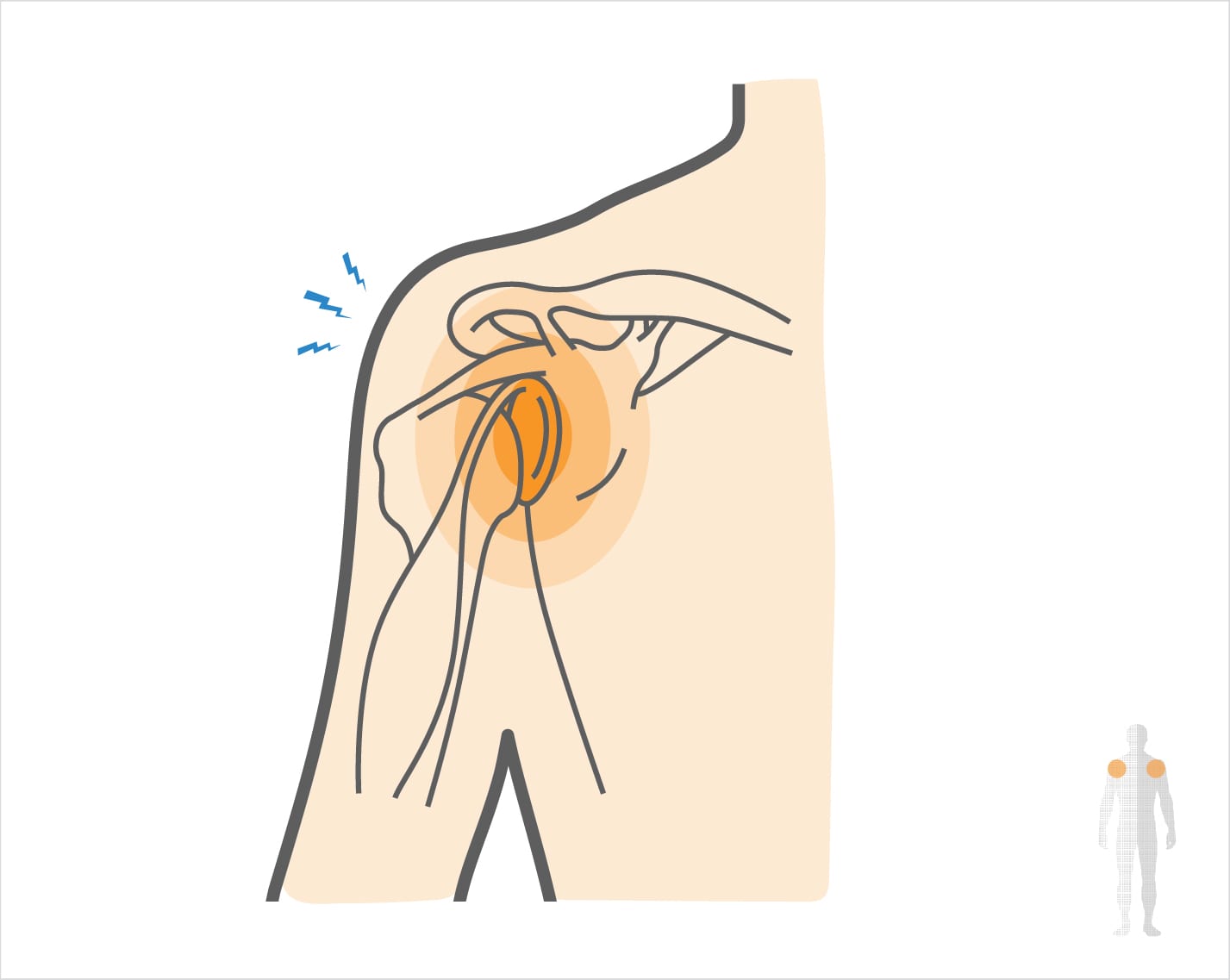
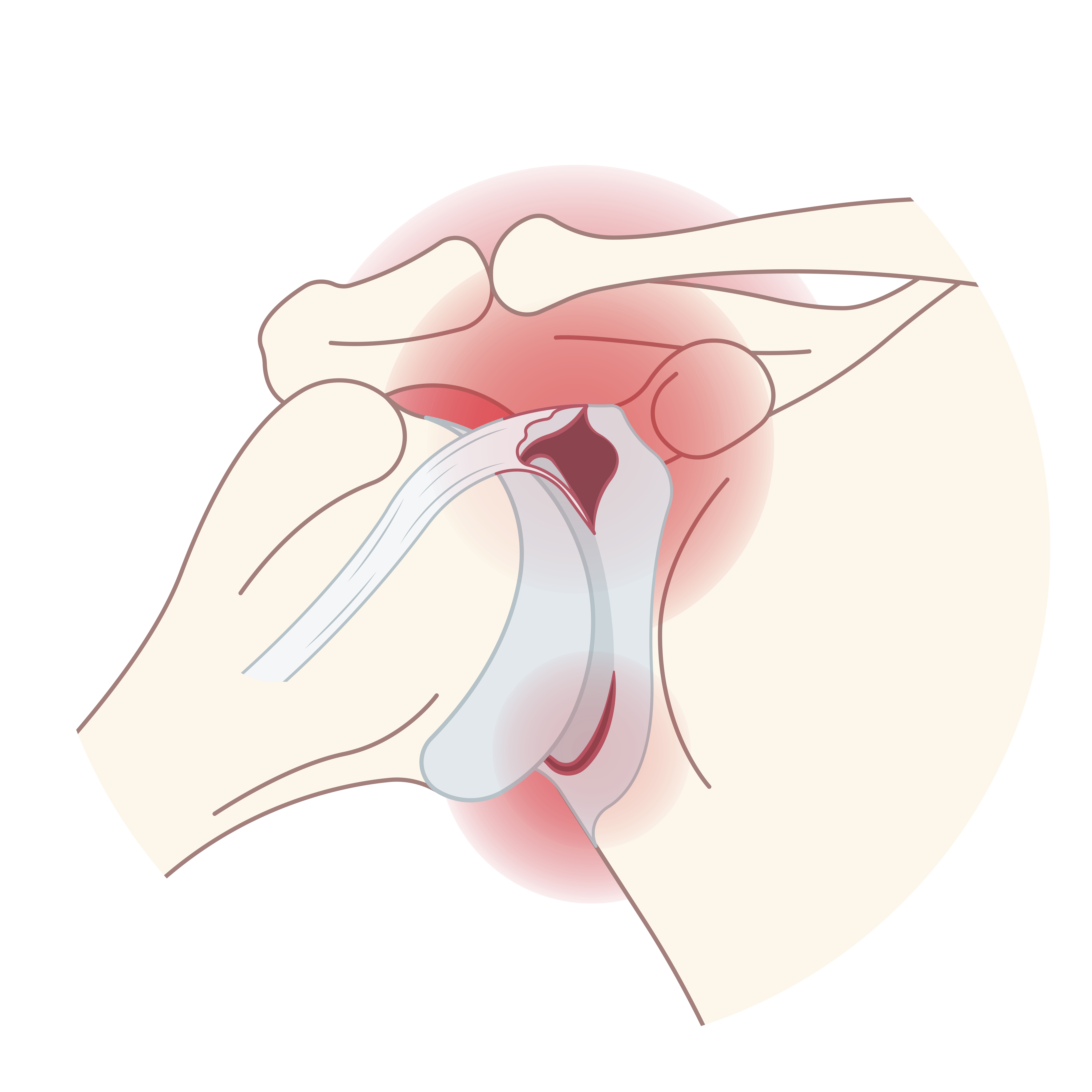
The shoulder joint is formed where three bones meet: the humerus (long bone that forms the upper arm), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the clavicle (collarbone). The head of the humerus bone fits inside of a cavity of the scapula called the glenoid fossa. Inside the glenoid fossa is a ring of cartilage, called the labrum. The labrum serves multiple important functions for the shoulder, like:
• Providing stability for the shoulder joint by “hugging” the head of the humerus
• Providing cushion for the shoulder joint, protecting the humerus bone and the scapula from grinding against each other
• Serving as a connection point for various shoulder ligaments
• Serving as a connection point for the long head of the bicep tendon
When the top (superior) portion of the shoulder labrum tears, this is referred to as a SLAP tear. The superior portion of the labrum is where the long head of the biceps tendon attaches. This tendon may also be injured in a more severe SLAP tear.
A SLAP tear can occur either in the front (anterior) or back (posterior) portion of the labrum.