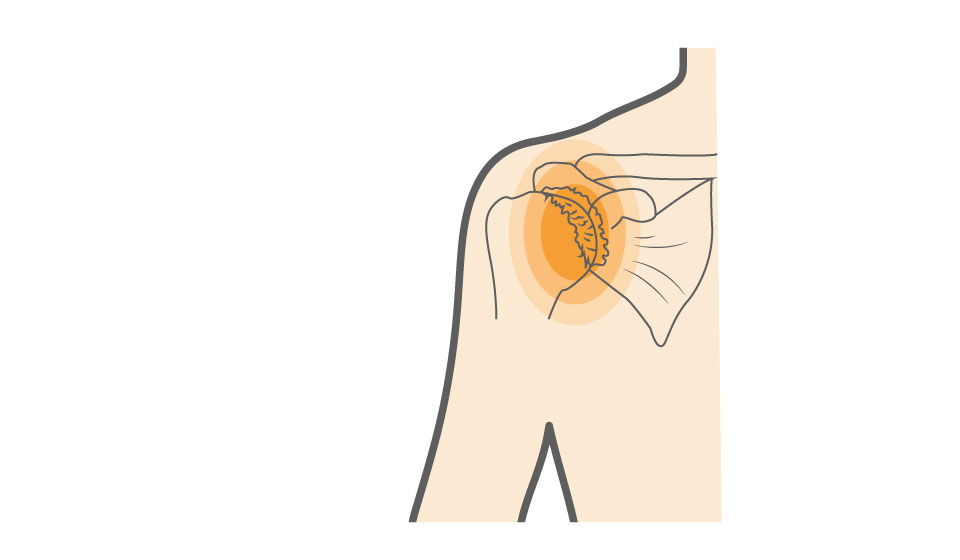
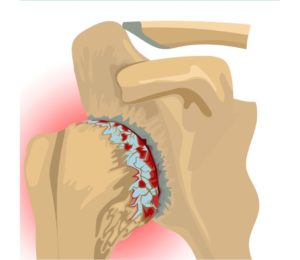
Shoulder joint arthritis, also called glenohumeral joint arthritis, is a condition characterized by damage to the cartilage in the shoulder joint. The glenohumeral joint is a major joint where the head of the humerus (the upper arm bone) rests in the glenoid cavity of the scapula (the shoulder blade). The ends of the bones at the joints are covered with a smooth tissue called cartilage that helps the bones of the joint glide easily and without friction. When cartilage is damaged, the bones can start to rub against each other, causing inflammation, shoulder grinding, and further damage to the joint.
There are three types of arthritis that affect the shoulder:
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of the joint’s cartilage due to aging is the most common cause of degenerative shoulder joint conditions.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disease where the body attacks itself and leads to degeneration of the joints.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: A form of osteoarthritis that develops after someone experiences an injury to the joint that damages the cartilage and changes the normal mechanics of the joint, leading to further wear and tear of the cartilage.
With all types of arthritis, the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones of the joint is lost. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis to affect the shoulder