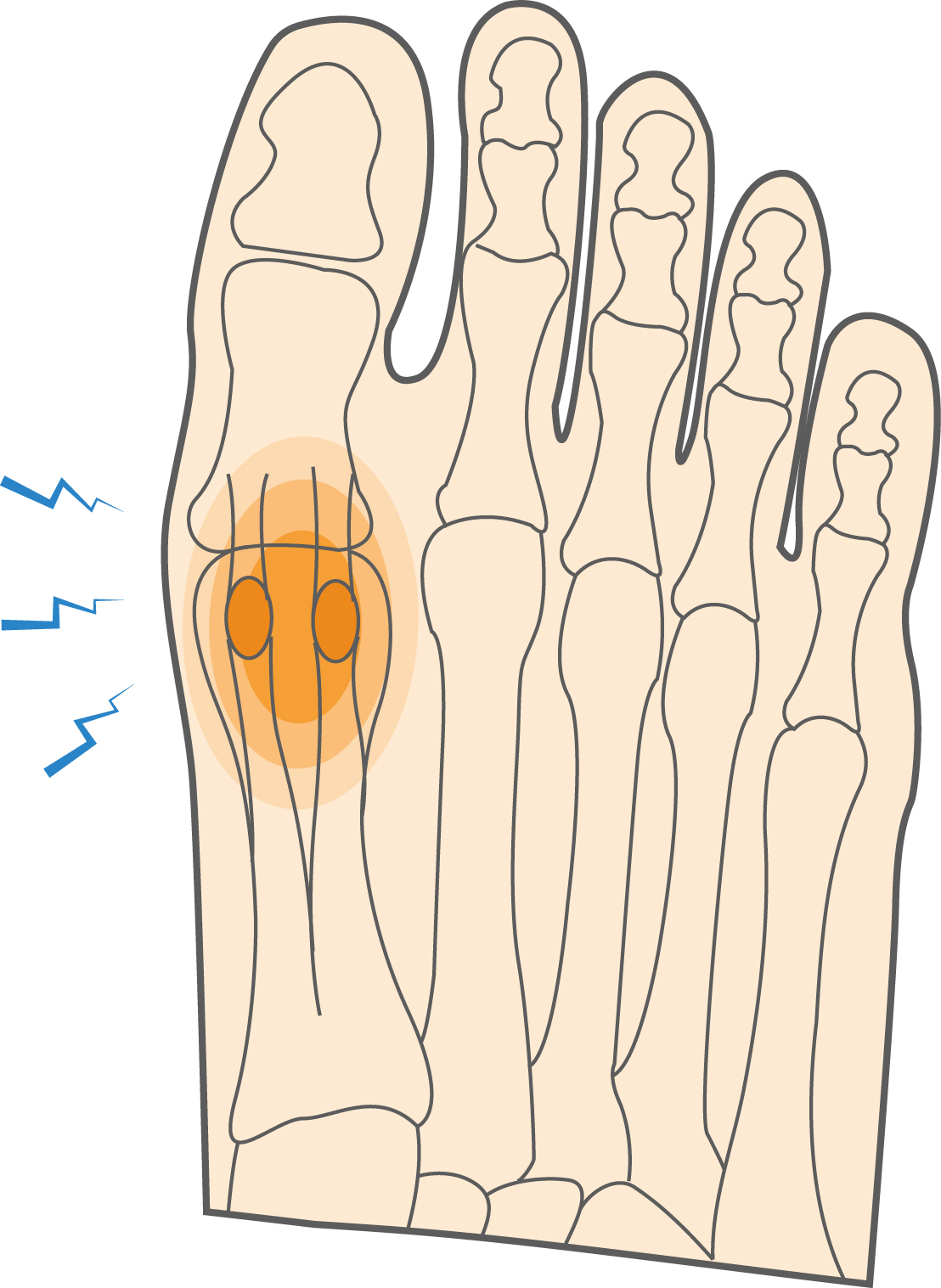
The sesamoid complex in the foot consists of a pair of bones that are embedded into the muscle under the big toe. They act as weight absorbers for the ball of the foot and come into play during sporting activities such as running or jumping.
The tibial sesamoid is the larger of the two and sits within the medial head of the flexor hallucis brevis muscle; the fibular sesamoid is the smaller bone and is situated within the lateral head.
Sesamoiditis is an inflammation of the sesamoid bones, a painful condition that can cause further complications if left untreated.