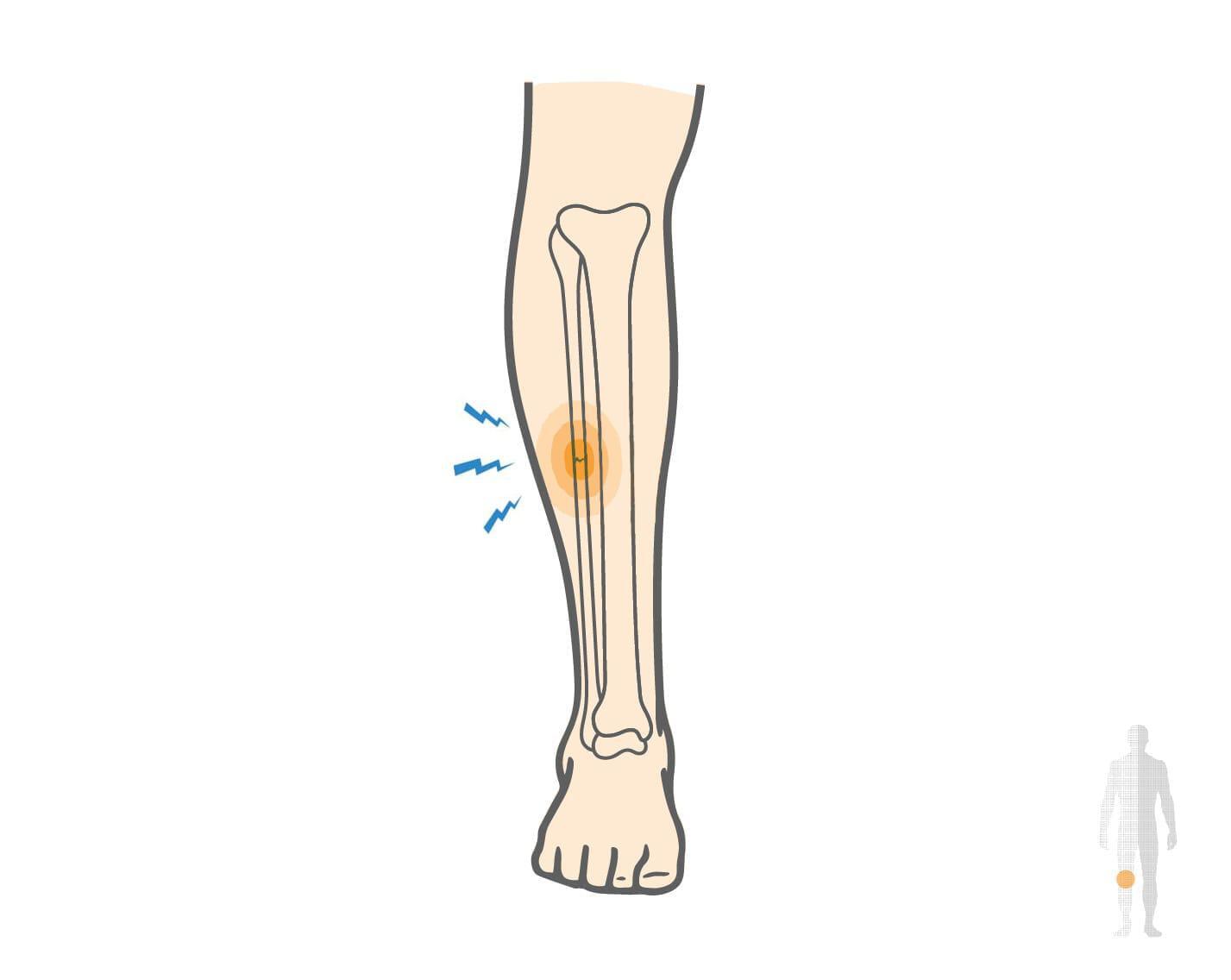
Proximal Fibula Fracture Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
The fibula is a long, thin bone located on the outside of the lower leg, running from just below the knee to the ankle. It is the smaller of the two lower-leg bones, with the tibia (shin bone) carrying most of the body’s weight. Fibula fractures can occur anywhere along this bone, depending on the type and force of injury. A proximal fibula fracture occurs near the top of the fibula, close to the outside of the knee. This injury is sometimes called an upper fibula break. In many cases, the fibula is fractured without damage to the ankle or tibia. When this happens, it is known as an isolated proximal fibula fracture. These fractures often heal well with proper care and do not usually require surgery.
Start with our quick Symptom Assessment or connect directly with an Upswing Coach today.
Request an AppointmentReady to take the next step?
Start your symptom assessment or connect with a coach instantly.
Find Relief TodayOverview
The fibula plays an important role in leg stability, muscle attachment, and ankle support. Although it does not bear much weight, damage to this bone can still cause significant pain and limit movement. Fibula fractures range from small cracks, such as a fibula hairline fracture or fibula stress fracture, to complete breaks caused by a strong impact.
The fibula can fracture near the knee, in the middle of the leg, or near the ankle. When the fracture occurs at the ankle, it is often referred to as a lateral malleolus fracture. Proximal fibula fractures are different because they occur higher up and may not directly affect ankle movement.
What causes What causes a Proximal Fibula Fracture and How to Treat it??
A proximal fibula fracture is most commonly caused by a direct blow to the outside of the leg, such as during a fall, collision, or contact sport. The force of impact can crack or break the fibula near the knee.
In some cases, a twisting injury to the ankle can also lead to a proximal fibula fracture. This happens because rotational force travels up the leg and places stress on the fibula. Repeated stress over time, especially in athletes, can also cause a fibula stress fracture, which may begin as a small crack and worsen if activity continues.
How the Injury Occurs
A proximal fibula fracture occurs when force is applied directly or indirectly to the outer leg. A sudden hit can overwhelm the bone’s strength, causing an immediate break. Twisting injuries place rotational stress on the fibula, which may result in a fracture even without a direct impact. Overuse injuries, such as running or jumping repeatedly without adequate rest, can lead to a fibula stess fracture.
Common Everyday Causes
Outside of sports, proximal fibula fractures can happen during routine activities, including:
- Slipping or falling onto the outer leg
- Accidental impact against furniture or hard surfaces
- Twisting the leg while walking on uneven ground
- Repetitive strain from prolonged standing or walking
Even minor trauma can cause a fracture in people with weaker bones or low bone density.
Sports Where Proximal Fibula Fractures Are Common
Proximal fibula fractures are more common in sports that involve contact, sudden direction changes, or high-impact falls, such as:
- Soccer: Direct kicks or collisions with other players can strike the outer leg
- Football: Tackles and helmet contact often result in blunt force injuries
- Skiing: Falls and twisting motions place stress on the lower leg
- Rugby: High-impact collisions increase the risk of fibula fractures
Athletes in these sports are also at higher risk for fibula stress fractures due to repetitive loading.
Symptoms
The most common symptom is pain on the outside of the knee or upper leg, which usually starts immediately after injury. The pain may worsen with movement or pressure. Other common symptoms include:
- Swelling and bruising along the outer leg
- Tenderness to touch over the fibula bone
- Difficulty bearing weight, especially when walking or standing
- Aching or sharp pain that does not improve with rest
In some cases, swelling and bruising may spread down the leg over time.
When to see a doctor
You should see a doctor if you experience pain after a direct blow to the outer leg or knee, notice significant bruising or swelling, or cannot put weight on the leg. Pain when pressing on the fibula is a strong sign of injury. These symptoms may indicate a proximal fibula fracture, a fibular head fracture, or another knee-related injury.
Your doctor will review how the injury happened, examine your leg, and order X-rays to confirm the diagnosis. It is especially important to evaluate the ankle, as fibula fractures can sometimes be linked to ankle injuries.
Non-operative treatment
Most isolated proximal fibula fractures heal without surgery. Non-operative treatment usually includes rest, ice, and limiting weight-bearing for a short period. A compression wrap, walking boot, or brace may be used to protect the leg and improve comfort while healing.
As pain decreases, gentle movement is encouraged to prevent stiffness. Physical therapy exercises help restore strength, flexibility, and balance.
Try these exercises to help address your condition:
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely needed for an isolated proximal fibula fracture. However, if the fracture occurs along with an ankle injury or instability, surgical treatment may be required to restore proper alignment and function.
Recovery
Recovery from an isolated proximal fibula fracture typically takes about six weeks, depending on the severity of the injury and activity level. Athletes may need additional time and structured physical therapy before safely returning to sports. With proper treatment, most people recover fully and regain normal leg function.
Dr. Jay Kimmel is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine, arthroscopic surgery, and shoulder and knee disorders. He completed his orthopedic training at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center and a Sports Medicine Fellowship at Temple University.
Dr. Kimmel previously served as the Director of the Connecticut Sports Medicine Institute at Saint Francis Hospital and has held faculty appointments as Clinical Assistant Professor in the Departments of Orthopedics and Family Medicine at the University of Connecticut. He has extensive experience caring for athletes as a team physician for high school and collegiate programs and continues to teach in the athletic training departments at Westfield State University and Springfield College.
Find the Support You Need — Right When You Need It
Whether you’re managing pain for the first time, need ongoing guidance, or require expert medical care, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
ORTHO DIRECT
Video visit with an orthopedic doctor for advice and a care plan.
$30
/MonthMRI DIRECT
Fast, affordable MRI with orthopedic review. No insurance required.
$499
/MonthFrequently Asked Questions
Can a fibular head fracture heal without surgery?
Yes, most fibular head fractures heal well with rest and conservative care.
Is a proximal fibula fracture like this common in athletes?
Yes, especially in contact and high-impact sports.
How long does it take to recover from a proximal fibula fracture?
Most people recover in about six weeks.
What are the signs of an upper fibula break?
Pain, swelling, fibula fracture bruising, and difficulty bearing weight are common signs.