Posterior impingement of the elbow joint usually occurs due to repeated extension of the elbow. This syndrome may lead to the development of bone spurs (extra bone that forms on the edge of an existing bone) and inability to extend the elbow.
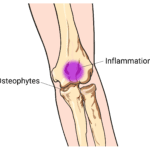
Posterior impingement of the elbow joint usually occurs due to repeated extension of the elbow. This syndrome may lead to the development of bone spurs (extra bone that forms on the edge of an existing bone) and inability to extend the elbow.

Repetitive throwing motions force the bony tip of the elbow, called the olecranon, to repeatedly jam into the fossa (pit at the back of the elbow). This motion causes wear and tear and inflammation of the tissues at the back of the elbow joint. This repeated contact can result in olecranon impingement and contribute to elbow extension pain. Baseball pitchers and tennis players are often at risk for this condition due to the repetitive extension of the elbow required in their sports.
Signs and symptoms of posterior impingement syndrome of the elbow include:
If you have pain in the back of your elbow associated with losing the ability to straighten your elbow, consult your doctor. A physical examination usually may lead to a diagnosis of elbow impingement. Your doctor may also order an X-ray to help identify if bone spurs are present and an MRI to rule out other causes of your symptoms, especially in cases related to throwing injury or suspected olecranon impingement.
Generally, conservative treatment is recommended for posterior impingement syndrome, including:
You can also try these exercises at home to stretch and strengthen the muscles surrounding the elbow:
Surgical treatment for posterior impingement syndrome may occasionally be needed in throwing athletes. If conservative treatment options are ineffective, particularly if you have bone spurs that require removal, your doctor may recommend arthroscopic surgery. This type of surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that allows surgeons to remove bone fragments causing damage to your elbow, especially in cases involving olecranon impingement and persistent elbow extension pain.
For mild cases, athletes usually can return to sports within six weeks with conservative treatment. If you undergo surgery because conservative treatment options are ineffective, a longer recovery time is required. After surgery, it usually takes three to six months to return to play, depending on the degree of joint overload and how your elbow responds to post-operative care.
This condition typically develops through consistent use of the elbow in high-extension activities like throwing, serving, or weightlifting. Over time, this motion can lead to subtle changes in the joint, such as bone spur formation, often referred to as olecranon impingement.
Athletes in sports like baseball, tennis, or softball—where frequent arm extension is part of the game—often benefit from understanding how to support their elbow health. Early awareness helps maintain peak performance and mobility.
A combination of rest, activity adjustments, gentle stretching, and physical therapy helps encourage optimal recovery. These approaches reduce joint overload while building strength and flexibility in the elbow.
Absolutely. Many people resume their usual sports and routines with proper care and a tailored recovery plan. Whether through conservative care or guided support from a healthcare provider, returning to the activities you enjoy is an achievable goal.