Olecranon Bursitis Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
Olecranon bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa overlying the olecranon process of the elbow, commonly resulting from trauma, repetitive pressure, or infection. Clinically, it presents with localized swelling, pain, and a limited range of motion. Management includes conservative measures, aspiration, or surgical intervention in refractory or septic cases.
Start with our quick Symptom Assessment or connect directly with an Upswing Coach today.
Request an AppointmentReady to take the next step?
Start your symptom assessment or connect with a coach instantly.
Find Relief TodayOverview
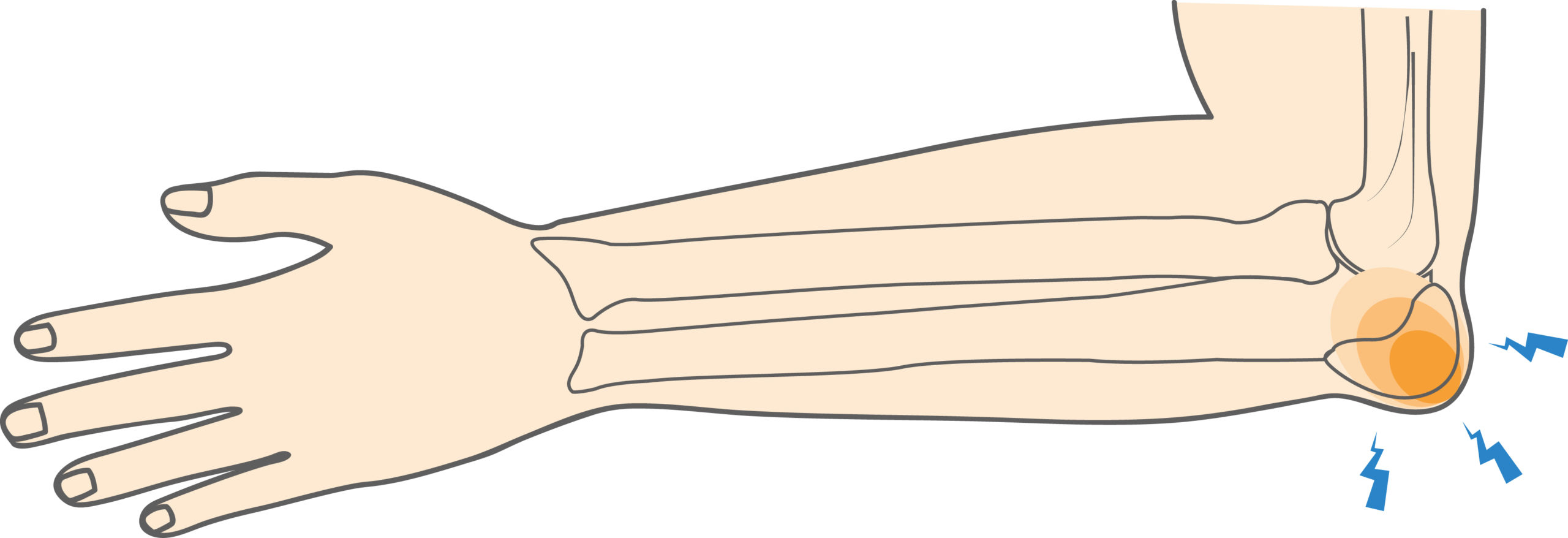
The olecranon bursa, a small, thin, fluid-filled sac, is situated at the tip of the elbow, overlying the olecranon process. Bursae are distributed throughout the body and serve a critical function in minimizing friction between bones and surrounding soft tissues during movement.
Olecranon bursitis arises when this specific bursa becomes inflamed or swollen, increasing pressure within the elbow region. As a result, affected individuals commonly experience localized pain, tenderness, and discomfort, often accompanied by restricted motion, particularly during activities that involve bending or leaning on the elbow.
What causes Olecranon Bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis typically develops due to direct trauma to the posterior aspect of the elbow, leading to fluid accumulation and swelling within the bursa. Repetitive stress or prolonged pressure on the elbow can also contribute to its development.
- How the Injury Occurs: The bursa becomes inflamed when subjected to repeated friction, impact, or pressure, resulting in localized swelling, pain, and reduced mobility.
- Common Everyday Causes:
- Office workers resting their elbows on hard desks for prolonged periods.
- Tradespeople like plumbers or carpenters who frequently lean on their elbows during work.
- Individuals recovering from elbow fractures or other trauma where swelling persists.
- Office workers resting their elbows on hard desks for prolonged periods.
Individuals at Higher Risk:
- Contact Sport Athletes (e.g., football players): Frequent impacts increase the likelihood of bursae trauma and swelling.
- Athletes Who Land on Elbows (e.g., volleyball players): Repeated falls or dives onto hard surfaces can irritate the bursa over time.
- Those Engaging in Repetitive Motions (e.g., baseball pitchers): Continuous flexion and extension place stress on the elbow, promoting inflammation.
Elbow bursitis is common in these sports:
- Football: Frequent tackles and impacts can traumatize the elbow, leading to inflammation of the bursa.
- Lacrosse: Collisions and falls during play place repeated stress on the elbow bursa.
- Baseball: Repetitive throwing motions strain the elbow, increasing susceptibility to bursitis.
- Basketball: Falling or landing on the elbow during play can irritate the bursa.
- Volleyball: Dives and repetitive elbow contact with the floor contribute to inflammation.
- Wrestling: Constant pressure and direct blows to the elbow during grappling elevate bursitis risk.
Symptoms
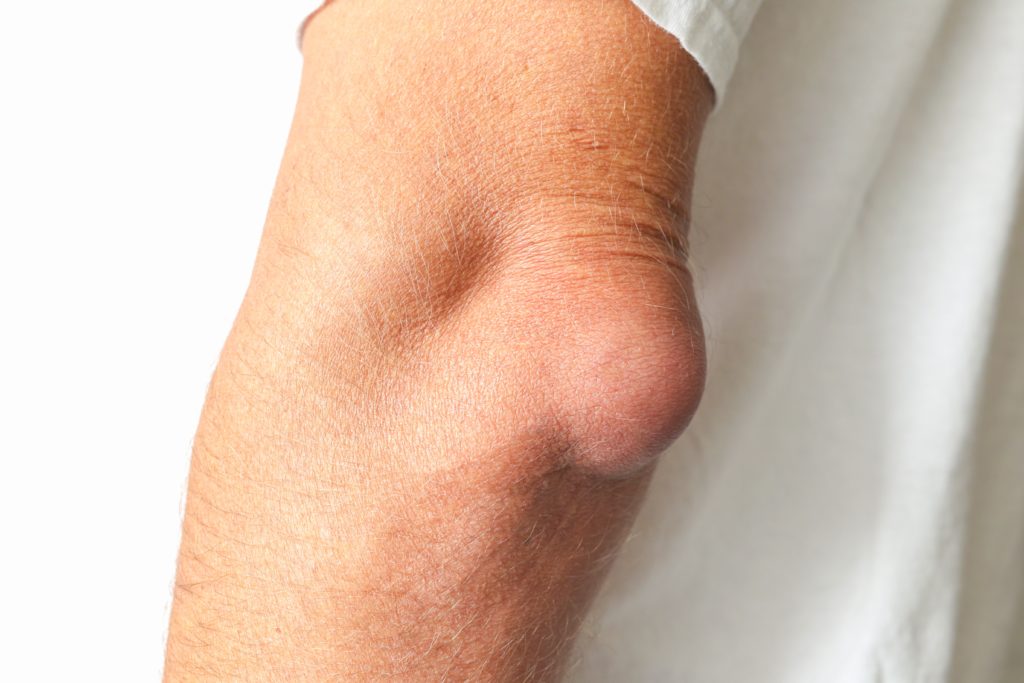
The most prominent symptom of elbow bursitis is localized swelling over the elbow tip. In cases related to chronic conditions, such as repetitive motion, it may develop gradually over time. Conversely, swelling following an acute injury often appears rapidly and can range from mild to severe.
The surrounding structures of the elbow joint generally remain unaffected. However, as the inflamed bursa enlarges, it exerts pressure on adjacent tissues, resulting in pain. This discomfort typically worsens with activity, direct pressure, or during elbow flexion and extension.
When to see a doctor
Olecranon bursitis can often be managed with home care. However, a medical evaluation is necessary if specific symptoms develop. It is essential to distinguish between a septic and an aseptic bursa. The presence of fever, general malaise, redness, warmth, or other systemic symptoms alongside elbow swelling may indicate septic bursitis, which requires prompt medical attention.
Even without a fever, a worsening elbow condition warrants a medical appointment. During the examination, a physician will assess for tenderness and swelling over the olecranon and evaluate the range of motion.
Diagnostic imaging may also be recommended. X-rays can help identify fractures or bone spurs, while an ultrasound can provide detailed visualization of inflammation within the olecranon bursa.
Non-operative treatment
If your doctor suspects your bursitis is caused by infection, they may want to aspirate the bursa or remove fluid using a thin needle. Removing the fluid will help alleviate the symptoms. Testing the fluid can help determine if an antibiotic is needed to treat elbow bursitis. If the bursitis is not due to infection then the following treatment is recommended.
- Rest: It is important to relieve pressure on the elbow to allow the bursae to heal. Athletes, particularly those who play high-impact sports, should discontinue activities that aggravate their elbow. An elbow pad may be helpful to protect the elbow.
- Ice: To help reduce swelling, apply ice packs to your elbow three to four times a day for 20 minutes.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate symptoms.
- Aspiration: Even if your bursa does not seem infected, your physician may aspirate it (remove the fluid with a needle) to resolve the problem more quickly.
Try these exercises to help address your condition:
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Surgical Treatment
Surgical intervention for olecranon bursitis is uncommon and generally considered only when conservative treatment methods fail to relieve symptoms. In such cases, a physician may recommend excision of the inflamed bursa to prevent recurrent swelling, persistent pain, or functional limitations. Surgery is typically reserved for chronic , severe bursitis or septic bursitis that does not respond to rest, medications, or other non-invasive therapies.
Recovery
Following conservative or surgical treatment, full recovery is contingent upon resolving swelling and restoring pain-free elbow movement. Patients can generally expect three to six weeks to recover before resuming normal activities or athletic participation if surgery is performed.
During this time, protective measures, such as wearing an elbow pad, can help prevent additional trauma and support the healing process, while gradual rehabilitation exercises assist in regaining strength and flexibility in the joint.
Dr. Jay Kimmel is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine, arthroscopic surgery, and shoulder and knee disorders. He completed his orthopedic training at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center and a Sports Medicine Fellowship at Temple University.
Dr. Kimmel previously served as the Director of the Connecticut Sports Medicine Institute at Saint Francis Hospital and has held faculty appointments as Clinical Assistant Professor in the Departments of Orthopedics and Family Medicine at the University of Connecticut. He has extensive experience caring for athletes as a team physician for high school and collegiate programs and continues to teach in the athletic training departments at Westfield State University and Springfield College.
Find the Support You Need — Right When You Need It
Whether you’re managing pain for the first time, need ongoing guidance, or require expert medical care, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
ORTHO DIRECT
Video visit with an orthopedic doctor for advice and a care plan.
$30
/MonthMRI DIRECT
Fast, affordable MRI with orthopedic review. No insurance required.
$499
/MonthFrequently Asked Questions
Is it safe to stay active with mild symptoms?
If you don't put pressure on the elbow, activity that avoids direct impact is usually safe.
Will I need surgery for elbow bursitis?
Very unlikely. Surgery is rare and only considered when other treatments don't work. Most people recover fully with non-invasive care.
Can I prevent bursitis from coming back?
Yes, you can! Using elbow pads, avoiding prolonged pressure, and following a simple exercise routine can reduce the chance of recurrence.
Is it okay to return to sports after bursitis?
You're good to go once the swelling is gone and you're pain-free with full motion.