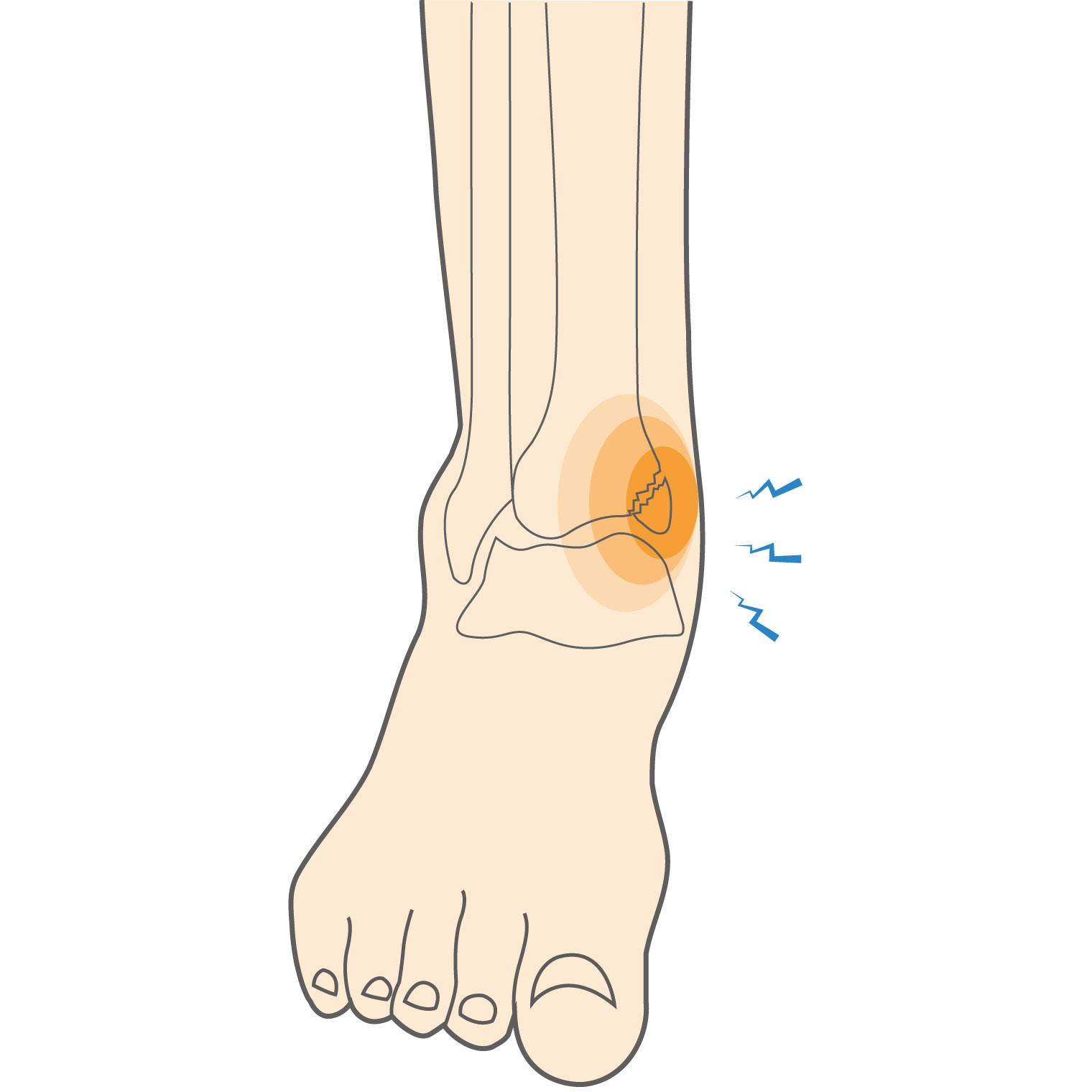
The medial malleolus is the bone on the inner side of your ankle. It is the end of the tiba (shin bone). The tibia(shin bone) bears approximately 90% of your body weight.
An isolated medial malleolus fracture or break is rare and often occurs in combination with a break or fracture of the fibula, the long, thin bone on the outside of the ankle. If you are unable to bear weight and have pain ONLY on the inside bone of your ankle, this can be due to an inside ankle break or fractured medial malleolus.