A low back strain occurs when muscles or tendons, the fibrous cords that connect muscle to the vertebrae of the spine, get twisted, stretched, or torn. Back strains are common, especially among athletes. The muscles that make up the upper and lower back support the spine and can easily get stretched, overloaded, or twisted during physical activity. A Back muscle injury can range from mild to severe. With treatment, athletes are usually back in action within weeks.
Lower Back Strain Injuries Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
A low back strain occurs when soft tissue connected to the vertebrae of the spine is stretched beyond its capacity. Back strains are common, especially among athletes.
Overview
Overview
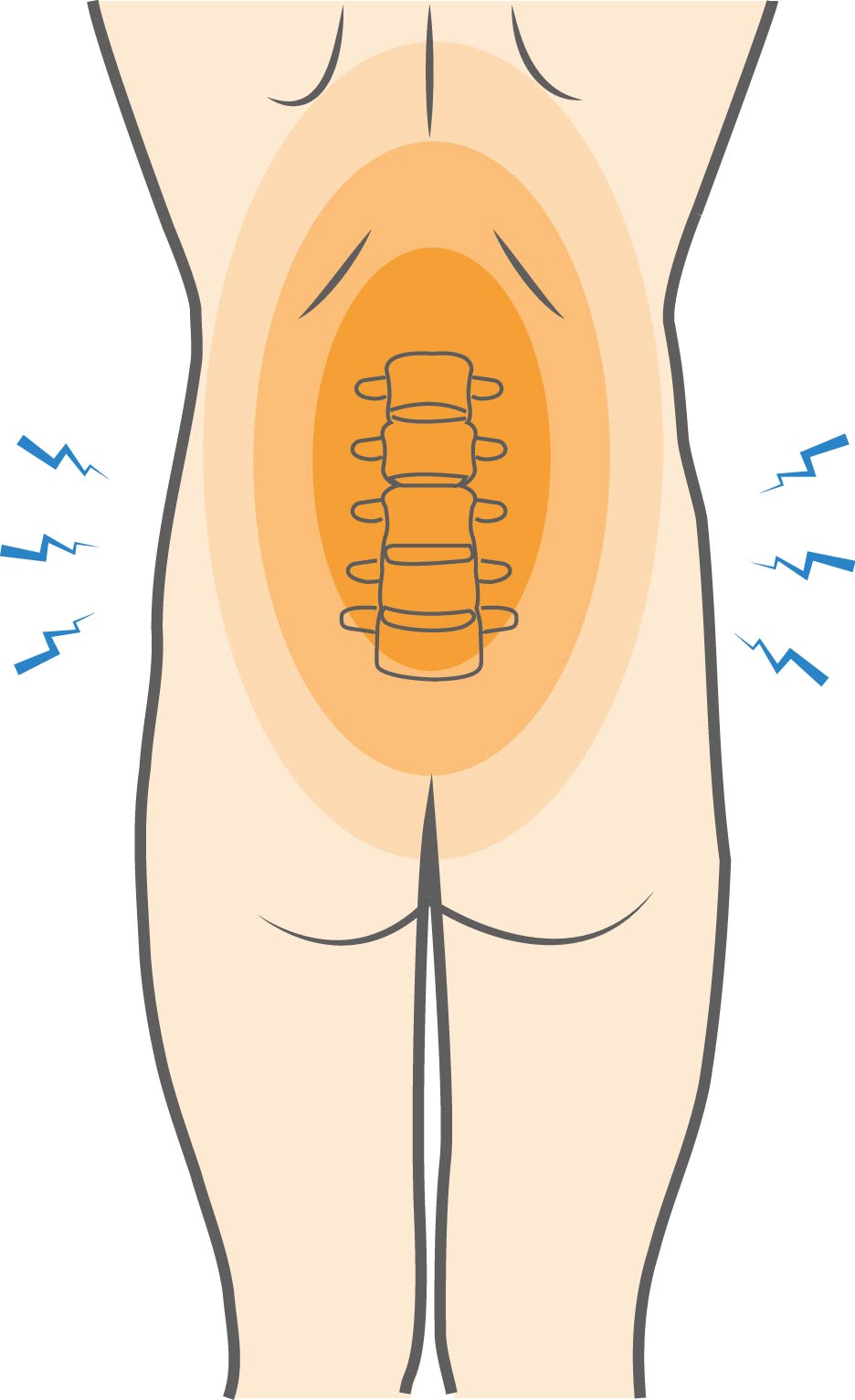
What causes Lower Back Strain Injuries?
Spinal strain injuries often occur because muscles in the back are overloaded. This can happen due to overuse, overstretching, or a sudden twist of the muscle. Chronic, repetitive activity can contribute to lower back strain injuries and postural stress.
Lower back spinal strain injuries are most common in these sports:
- Racket sports (tennis, racketball, squash)
- Hockey
- Football
- Rugby
- Basketball
- Baseball
- Weightlifting
Symptoms
Lower back spinal strain injuries often cause pain and weakness. This and other symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the strain. Common symptoms also include:
- Pain that gets worse with movement
- Tenderness
- Muscle spasms
- No radiation of the pain down the legs
- No numbness or tingling in the legs
- No weakness in the legs
When to see a doctor
If you experience symptoms of a back muscle injury or lower back tightness that don’t resolve after a week or prevent you from doing your normal activities, you should see your doctor. You should also seek medical treatment if you experience radiating leg pain, as this symptom may suggest that you may have a more serious injury such as sciatica or nerve damage.
Usually, a diagnosis can be made by taking a medical history and conducting a physical examination. Your doctor will want to examine your back and look for signs of a strain, such as inflammation and tenderness. An X-ray and/or MRI may be ordered to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Non-operative treatment
Treatment of lower back strain injuries always involves non-surgical measures to allow injured muscles to heal properly. Conservative treatments include:
- Rest from activities and sports that place strain on the back
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Heat to loosen up the muscles
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, to help relieve pain and inflammation
- Muscle relaxant medications to reduce spasm
- Physical therapy (such as stretching exercises and sports massage), especially for more severe strains
Try these exercises to help address your condition:
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Recovery
After 24–48 hours, and after pain subsides, most athletes can start to get back to physical activity. Longer-term bed rest may actually delay your recovery. Your doctor will advise you on a plan to get you back to a full recovery and return to play.
GET BACK TO WHAT YOU LOVE. FASTER
Sources
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/sprains-strains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries/
https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/lower-back-pain/pulled-back-muscle-and-lower-back-strain
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10265-back-strains-and-sprains
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/94387-overview
https://www.depuysynthes.com/patients/aabp/understandingconditions/musclestrainandsprain
Frequently Asked Questions
Can untreated low back strain lead to chronic pain or complications?
It can. While most strains heal with rest and conservative care, ignoring persistent symptoms or pushing through the pain can lead to poor movement patterns, compensatory injuries, and chronic back issues. Early treatment helps prevent a short-term injury from becoming a long-term problem.
What are the common signs that indicate misdiagnosis of a lumbar muscle pull?
If symptoms such as radiating leg pain, numbness, or bowel/bladder issues appear, this may indicate a more serious spinal condition misdiagnosed as a simple lumbar muscle pull.
How long should I wait before seeking treatment for lower back tightness?
If lower back tightness doesn’t improve within a few days of rest, ice, or OTC medication, you should consult a clinician to rule out more serious injuries or complications.
What is the expected recovery timeline for a low back strain?
Recovery from a lower back strain typically takes a few days to a few weeks with consistent therapy, though some cases may take longer depending on severity and compliance with treatment.