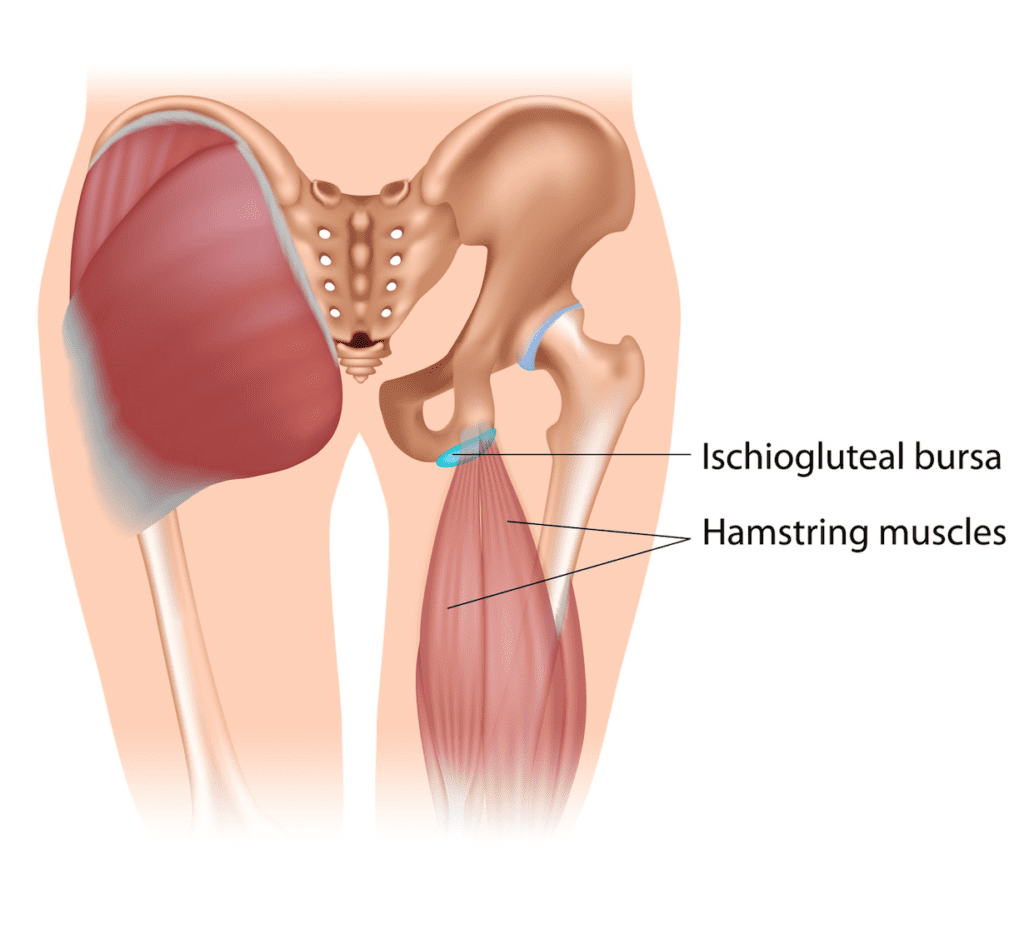
Ischial bursitis, also called ischiogluteal bursitis or “weaver’s bottom,” is a condition that causes pain in the buttocks. It’s caused by inflammation of the ischial bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between the hamstring muscles and the bony prominence of the pelvis that you sit on.
Ischial Bursitis Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
Ischial bursitis, also called ischiogluteal bursitis or “weaver’s bottom,” is a condition that causes pain in the buttocks. It’s caused by inflammation of the ischial bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between the hamstring muscles and the bony prominence of the pelvis that you sit on.
Overview
Overview
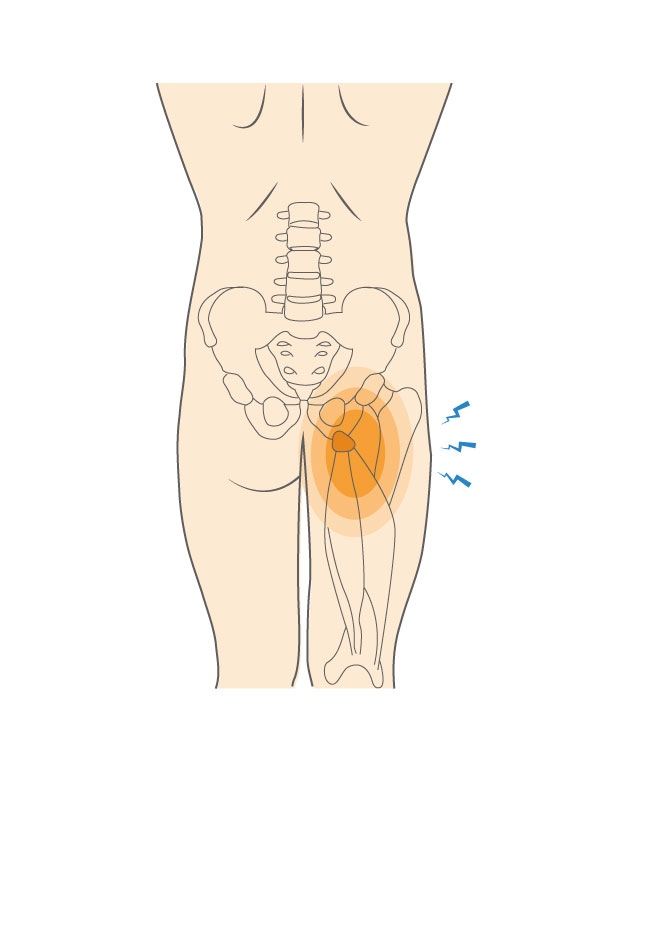
What causes Ischial Bursitis?
Ischial bursitis is often caused by repetitive stress on an ischial bursa, causing it to become inflamed. This can happen when sitting for long periods of time or playing sports that require repetitive motion, like running or cycling. An acute injury to an ischial bursa, due to a hard fall for example, can also cause this condition.
Ischial bursitis is most common in these sports:
• Cycling
• Running
• Soccer
Symptoms
Athletes with ischial bursitis usually experience a dull ache in the lower part of the buttocks on one side. This pain can spread down the back of the leg. Common symptoms also include:
• Pain that is felt when sitting, walking, or running after sitting
• Pain when running, especially sprinting or running uphill
• Pain when stretching the hamstring tendons
When to see a doctor
Athletes with symptoms of ischial bursitis may need to see their doctor. At your visit, you will be asked to describe your symptoms and physical activity. Your doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination, looking for areas of tenderness and pain. Occasionally, x-rays and other imaging tests will be ordered to rule out other sources of your pain, such as arthritis or more complex neurological issues, such as sciatica, spinal cord compression, or signs of lumbar tenosis.
Non-operative treatment
Treatment of ischial bursitis starts with rest and avoidance of aggravating activities. Other treatments include:
• Applying ice packs to tender areas
• Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, to relieve pain
• Gentle stretching exercises to improve flexibility
• A specialized pillow to use while sitting to reduce pressure on the bursa
• Physical therapy
• Corticosteroid injections to relieve pain
In cases where the symptoms persist, an ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection may be helpful. Avoid massage, as this will likely aggravate your condition.
Try these exercises to help address your condition:
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Surgical Treatment
If the bursa become infected, fluid from the bursa may need to be drained using a thin needle. In some cases, the bursa will need to be surgically removed. In the absence of an infection, however, surgery is rarely recommended.
Recovery
Recovery from ischial bursitis can take several weeks. Your recovery may include a graduated stretching and exercise program. Getting timely treatment and following the guidance of your physician and physical therapist will hasten your recovery.
GET BACK TO WHAT YOU LOVE. FASTER
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes ischial bursitis?
Ischial bursitis is usually caused by prolonged sitting on hard surfaces, repetitive activities like cycling or rowing, direct trauma to the buttock, or overuse of the hamstring muscles. It may also occur secondary to inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
How is ischial bursitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to rule out other conditions such as hamstring tendon injuries, sciatica, or lower back issues.
What is the best treatment for ischial bursitis?
Most cases are managed conservatively with rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms. In more persistent cases, corticosteroid injections or aspiration of the bursa may be recommended.
Can ischial bursitis become chronic?
If not properly treated, ischial bursitis can become a chronic condition. Recurring irritation or inadequate recovery may lead to ongoing discomfort. Long-term management may involve ergonomic adjustments, regular stretching, and strengthening exercises to support the surrounding muscles.