Iliotibial (IT) Band Tendonitis of the Knee Treatment
Iliotibial band tendonitis of the knee , also known as iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS), is a common overuse injury that causes pain on the outside of the knee. The iliotibial band is a thick band of connective tissue that runs from the hip to the knee and helps stabilize the leg during movement. Repetitive stress—especially from running—can cause irritation and inflammation of this band, leading to ITBS knee pain, particularly during activities like running, climbing stairs, or downhill movement.
Start with our quick Symptom Assessment or connect directly with an Upswing Coach today.
Request an AppointmentReady to take the next step?
Start your symptom assessment or connect with a coach instantly.
Find Relief TodayOverview
Iliotibial band tendonitis, commonly referred to as iliotibial band syndrome, is a condition caused by inflammation of the iliotibial band along the outer thigh. The IT band is made of strong fascia that connects the hip and gluteal muscles to the top of the shin bone (tibia).
As the largest fascia in the body, the iliotibial band plays a major role in stabilizing the knee during walking, running, and jumping. When it becomes tight or irritated, it can rub repeatedly against the outer part of the knee, leading to pain and inflammation. This is why IT band tendonitis is often associated with runners and is one of the causes of runner’s knee, especially when lateral knee pain is the primary symptom.
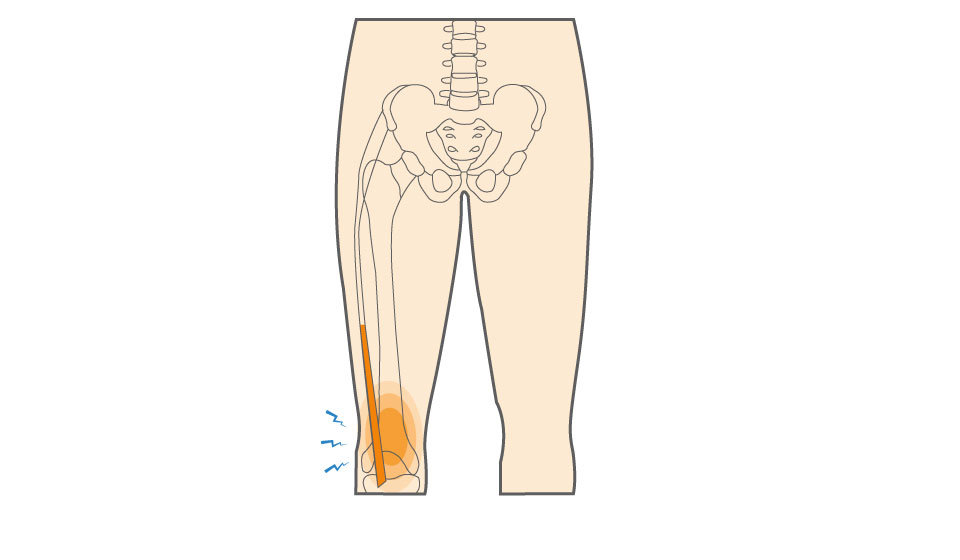
What causes Iliotibial (IT) Band Tendonitis of the Knee?
Iliotibial band tendonitis is a non-traumatic overuse injury, meaning it develops gradually rather than from a single injury. It most often occurs when the IT band is tight, overworked, or subjected to repetitive stress without adequate recovery.
Common causes include:
- Overtraining, especially sudden increases in mileage or intensity
- Running the same route repeatedly, particularly on sloped or cambered surfaces
- Worn-out or improper footwear that alters natural foot mechanics
- Improper foot mechanics, such as excessive pronation
- Inadequate stretching, especially of the hips, glutes, and thighs
If left untreated, this overuse injury can progress into iliotibial band friction syndrome, a painful condition characterized by persistent ITBS knee pain.
1. How the Injury Occurs
Repeated bending and straightening of the knee causes the tight IT band to rub against the outer knee, leading to irritation and inflammation over time.
2. Common Everyday Causes
- Prolonged walking or standing
- Sudden changes in physical activity
- Poor posture or muscle imbalances
Sports Commonly Associated with IT Band Tendonitis
- Long-distance or marathon running, due to repetitive knee motion
- Soccer, which involves sprinting and cutting
- Tennis, where frequent lateral movements stress the IT band
Athletes in these sports are particularly susceptible to iliotibial band syndrome.
Symptoms
You may have iliotibial band syndrome if you experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Pain on the outside of the knee, typically along the path of the IT band
- Pain that worsens with activity, especially running or cycling
- Increased pain when climbing or descending stairs
- A sharp or burning sensation near the outer knee
This lateral knee discomfort is a classic sign of ITBS knee pain and often starts mild before becoming more intense if activity continues.
When to see a doctor
If pain on the outside of your knee does not improve with rest or activity modification, you should see an orthopedic specialist. Persistent lateral knee pain may indicate inflammation of the iliotibial band rather than a simple muscle strain.
During the examination, your doctor will check for tenderness along the outer knee and assess leg flexibility. Special physical tests, such as the Ober’s test, may be used to evaluate IT band tightness.
Imaging Tests
To rule out other causes of knee pain, your doctor may recommend:
- X-ray – to exclude bone-related problems
- MRI – to assess soft tissues and confirm iliotibial band syndrome
Non-operative treatment
Iliotibial band syndrome treatment is almost always conservative and focuses on reducing inflammation, improving flexibility, and correcting contributing factors.
Common non-operative treatments include:
- Rest from aggravating activities
- Stretching is a key component of IT band tendonitis treatment
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen
To prevent recurrence, your doctor may also recommend:
- Correcting training errors, such as sudden mileage increases
- Wearing proper footwear to support healthy foot mechanics
These strategies are essential for managing runner’s knee and preventing ongoing ITBS knee pain.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Targeted exercises help improve flexibility and strengthen supporting muscles.
(Refer to the PDF Exercise Program below.)
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely required for iliotibial band tendonitis, as most patients respond well to conservative iliotibial band syndrome treatments. In very rare cases where symptoms persist despite prolonged non-operative care, surgical options may be considered to release tension in the iliotibial band or reduce friction at the outer knee. These procedures are typically reserved for severe, chronic cases of ITBS knee pain that do not improve with rest, stretching, physical therapy, and activity modification.
Recovery
You can safely return to training once you are pain-free and have regained flexibility and strength in the affected leg. Recovery should be gradual, with careful attention to warm-up routines and post-exercise stretching.
Taking these steps helps prevent future flare-ups of iliotibial band friction syndrome and effectively manages long-term lateral knee pain.
Dr. Jay Kimmel is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine, arthroscopic surgery, and shoulder and knee disorders. He completed his orthopedic training at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center and a Sports Medicine Fellowship at Temple University.
Dr. Kimmel previously served as the Director of the Connecticut Sports Medicine Institute at Saint Francis Hospital and has held faculty appointments as Clinical Assistant Professor in the Departments of Orthopedics and Family Medicine at the University of Connecticut. He has extensive experience caring for athletes as a team physician for high school and collegiate programs and continues to teach in the athletic training departments at Westfield State University and Springfield College.
Find the Support You Need — Right When You Need It
Whether you’re managing pain for the first time, need ongoing guidance, or require expert medical care, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
ORTHO DIRECT
Video visit with an orthopedic doctor for advice and a care plan.
$30
/MonthMRI DIRECT
Fast, affordable MRI with orthopedic review. No insurance required.
$499
/MonthFrequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of iliotibial band syndrome?
Pain on the outside of the knee that worsens with activity is the most common symptom.
How long does recovery usually take once diagnosed?
Most people improve within a few weeks with proper iliotibial band syndrome treatments.
How can I tell if I have IT band tendonitis or something else?
Pain localized to the outer knee during repetitive activity strongly suggests IT band involvement.
Is surgery ever needed if treatment is delayed?
Surgery is extremely rare, even in delayed cases, as most patients respond well to conservative care.