Extensor Tendonitis of the Foot Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Extensor tendonitis (foot) is an overuse injury characterized by inflammation of the tendons on the dorsum or top of the foot. It is commonly seen in athletes and individuals who perform repetitive dorsiflexion or bending their foot up and down. Clinical presentation includes top of the foot pain, swelling, and tenderness, which are aggravated by activity. Management typically involves activity modification, physical therapy, and, in refractory cases, surgical intervention to restore tendon function and relieve symptoms.
Start with our quick Symptom Assessment or connect directly with an Upswing Coach today.
Request an AppointmentReady to take the next step?
Start your symptom assessment or connect with a coach instantly.
Find Relief TodayOverview
Tendons are strong, fibrous cords that connect muscles with bones. The extensor tendons of your foot run across the top of your foot, connecting your lower leg to your toes. These foot tendons help you bend your foot up and raise your toes. Overuse of these tendons can cause inflammation, called tendon inflammation or extensor tendonitis of the foot.
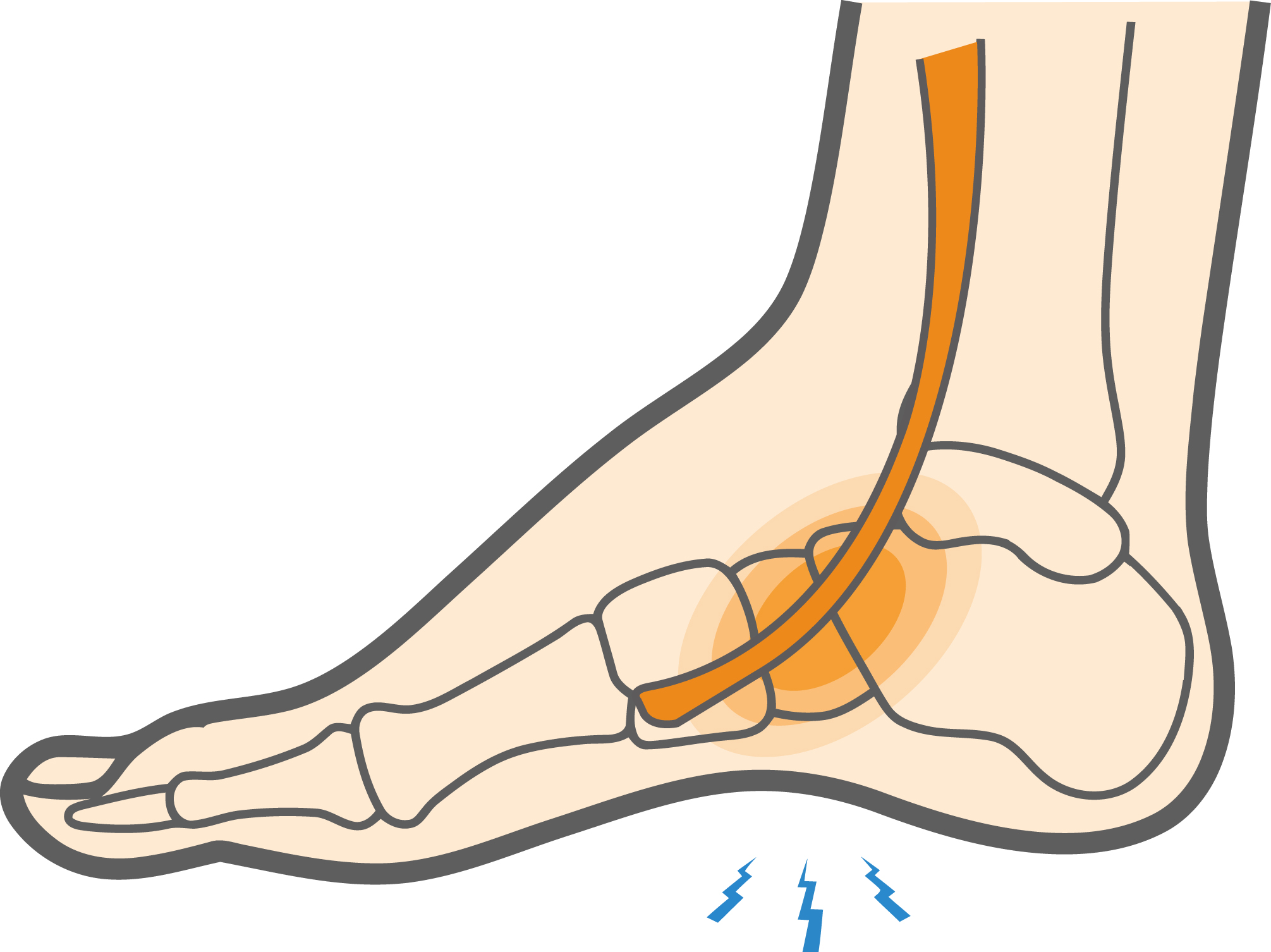
What causes Extensor Tendonitis of the Foot?
Extensor tendonitis of the foot develops primarily from repetitive overuse. Continuous dorsiflexion or bending the foot up, common in running and other high-intensity activities, can irritate the extensor tendons and trigger inflammation.
- How the Injury Occurs: Repetitive dorsiflexion or toe extension irritates the extensor tendons, causing inflammation and pain, often worsened by tight or poorly fitting footwear.
- Common Everyday Causes: Can develop from prolonged walking, standing, or wearing restrictive shoes that place continuous strain on the top of the foot.
Sports Commonly Associated with Extensor Tendonitis:
- Running: Repeated dorsiflexion during each stride places stress on the extensor tendons.
- Cross-country: Long-distance repetitive motion increases cumulative tendon load.
- Hockey and Figure Skating: Rapid ankle movements and forceful toe extension impose repeated stress on the tendons.
Symptoms
Extensor tendonitis of the foot typically presents as pain along the dorsal aspect of the foot, directly over the affected tendons. The discomfort usually develops gradually rather than after a single acute event. Additional characteristic features may include:
- Pain during toe extension or dorsiflexion: Engaging the extensor muscles often intensifies discomfort.
- Mild localized swelling: Swelling may increase during or after physical activity.
When to see a doctor
If you have persistent pain on the top of your foot that does not improve over time, you should consult your doctor.
During your visit, your doctor will perform a physical examination for signs of tenderness and tendon inflammation. They may also attempt to reproduce your symptoms by asking you to move your foot up and down against resistance.
X-rays may be taken to rule out other causes of your injury, such as bone spurs or a fracture. In some cases, additional imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and exclude an extensor muscle strain or other types of soft tissue injury.
Non-operative treatment
Treatment of extensor tendonitis of the foot is typically conservative. Your doctor may recommend taking a break from running or other activities that exacerbate pain on the top of the foot. Other common treatments include:
- Ice and elevation: Applying ice and elevating the foot to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
- Immobilization: Using a cast or special boot to support the foot.
- Medication: Taking anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the foot and improve function.
- Footwear: Ensuring shoes provide proper support and fit.
- Orthotics: Using inserts to correct any foot or ankle imbalances.
To support your recovery and improve tendon function, follow the exercises provided in the program below:
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is typically not required to treat extensor tendonitis of the foot.
In rare cases, it may be considered if symptoms do not improve with rest and other conservative treatments. Your doctor will determine whether surgical intervention is appropriate as part of your treatment plan.
Recovery
In most cases, normal activity can be resumed within a few weeks with rest and conservative treatment for extensor tendonitis of the foot. Addressing any underlying factors contributing to overuse is important to prevent recurrence.
Dr. Jay Kimmel is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine, arthroscopic surgery, and shoulder and knee disorders. He completed his orthopedic training at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center and a Sports Medicine Fellowship at Temple University.
Dr. Kimmel previously served as the Director of the Connecticut Sports Medicine Institute at Saint Francis Hospital and has held faculty appointments as Clinical Assistant Professor in the Departments of Orthopedics and Family Medicine at the University of Connecticut. He has extensive experience caring for athletes as a team physician for high school and collegiate programs and continues to teach in the athletic training departments at Westfield State University and Springfield College.
Find the Support You Need — Right When You Need It
Whether you’re managing pain for the first time, need ongoing guidance, or require expert medical care, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
ORTHO DIRECT
Video visit with an orthopedic doctor for advice and a care plan.
$30
/MonthMRI DIRECT
Fast, affordable MRI with orthopedic review. No insurance required.
$499
/MonthFrequently Asked Questions
Can extensor tendonitis be mistaken for another condition?
Extensor tendonitis of the foot can sometimes be misdiagnosed as a stress fracture or arthritis due to similar symptoms, such as pain in the top of the foot and swelling. Imaging tests like an MRI can help differentiate these conditions.
What is the main cause of extensor muscle strain?
Extensor muscle strain is typically caused by overuse injury, poor biomechanics, or excessive stress placed on the foot during activities like running or jumping.
Do I need to stop all physical activity during treatment?
Not necessarily. While rest is important, your doctor may recommend modifying your activities rather than stopping completely. Low-impact exercises and physical therapy can help manage tendon inflammation without worsening the injury.
How can I prevent extensor tendonitis of the foot in the future
Wearing well-fitting shoes, gradually increasing activity levels, using proper technique, and incorporating foot-strengthening exercises can help prevent extensor tendonitis of the foot and other overuse injuries.