Elbow Strain Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
An elbow strain occurs when the muscles or elbow tendons around the elbow are overstretched or partially torn, often due to sudden movement or overuse. This injury can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, and weakness, making it difficult to bend or straighten the arm. Most cases improve with rest, ice, activity modification, and gentle exercises. Early treatment helps prevent long-term complications and supports safe healing.
Start with our quick Symptom Assessment or connect directly with an Upswing Coach today.
Request an AppointmentReady to take the next step?
Start your symptom assessment or connect with a coach instantly.
Find Relief TodayOverview
An elbow strain occurs when the muscles or elbow tendons that help bend and straighten the elbow are stretched beyond their normal limits. This injury is sometimes called a “pulled elbow muscle.” When these tissues are overstretched, tiny tears can develop, which may also feel like an overextended elbow.
A strain affects the muscles or tendons, while an elbow sprain affects the elbow tendons and ligaments, the connective tissues that stabilize the joint. Both can happen from similar movements, but they involve different structures within the elbow.
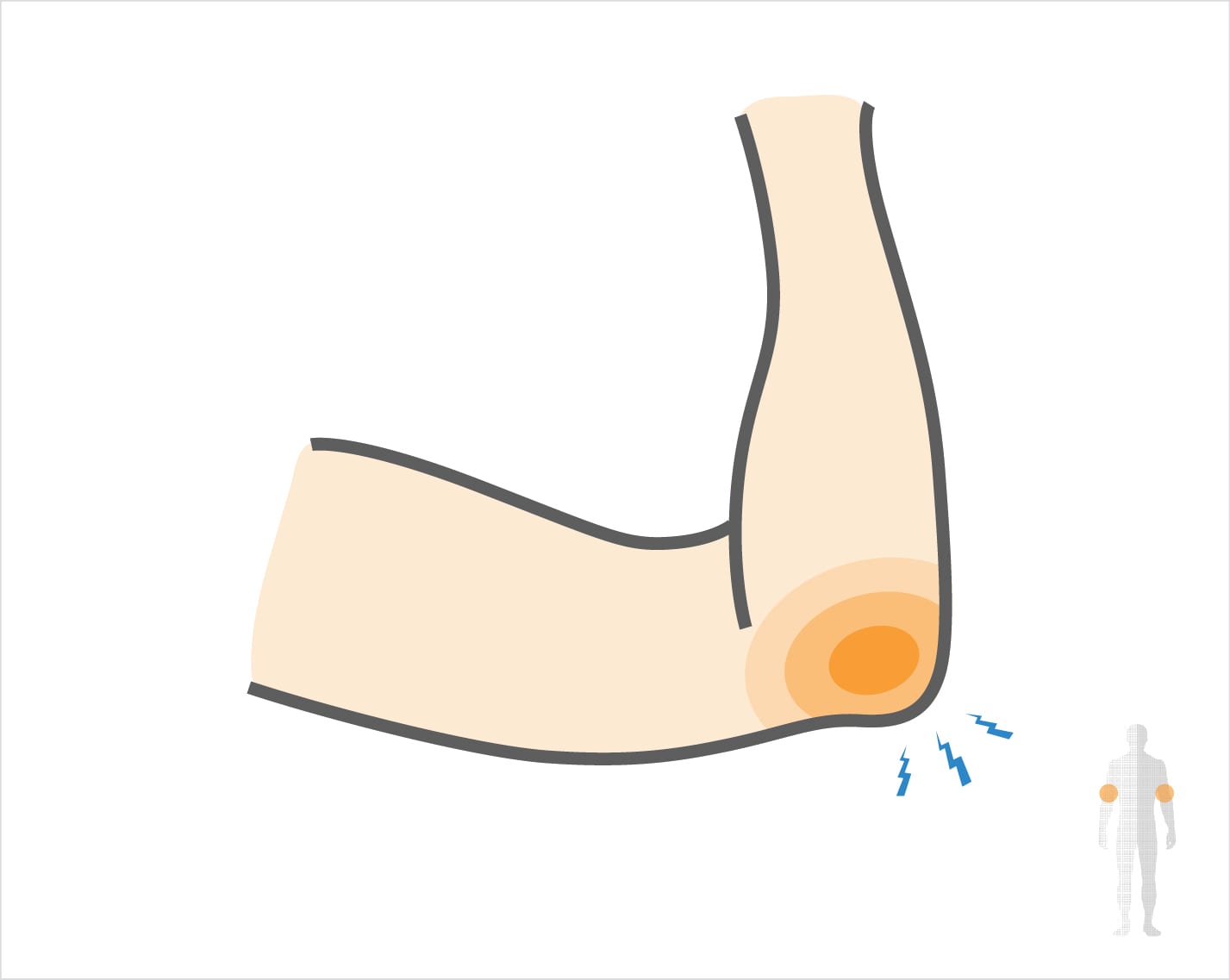
What causes Elbow Strain?
An elbow strain commonly develops from:
- Repetitive use: Sports like tennis or golf require repeated arm motions that can overload the muscles and tendons.
- Falling on an outstretched arm: Trying to break a fall can force the elbow beyond its limits, causing sudden stretching or tearing.
- Sudden, intense movement: Lifting, throwing, or exercising without warming up can strain the elbow quickly.
How the Injury Occurs: Elbow strains typically happen when the elbow moves in a forceful or repetitive way that overstresses soft tissues. This may include sudden extension, twisting, or high-impact arm movements. Over time, these small stresses can weaken the tissues and eventually lead to injury.
Common Everyday Causes: Beyond sports, elbow strains can result from daily activities like carrying heavy bags, pushing heavy doors, or performing repetitive work tasks.
Sports Where Elbow Strain Is Common
These sports regularly stress the arm and elbow, increasing the risk of strain:
- Basketball: Quick passes and overhead shots can strain elbow tendons.
- Football: Blocking, tackling, and sudden arm movement may overstretch the elbow.
- Golf: Repetitive swinging puts pressure on the forearm and elbow structures.
- Rugby: High-impact movements and falls increase the likelihood of elbow injury.
- Tennis: Repeated forehand and backhand swings stress the muscles that stabilize the elbow.
- Volleyball: Serving and spiking require strong, repetitive elbow motion.
Symptoms
You may have an elbow strain if you experience:
- Pain: Often felt during movement or when touching the injured area.
- Stiffness: Difficulty bending or straightening the arm fully.
- Weakness: Reduced strength when gripping or lifting objects.
- Symptoms that worsen with activity: Pain may increase with lifting, throwing, or pushing.
When to see a doctor
If you develop elbow pain after an injury or sudden movement, you can begin at-home care:
- Rest the elbow
- Ice the area several times a day
If symptoms continue to worsen, limit your range of motion, or interfere with daily activities, you should see an orthopedic specialist. During the examination, the doctor will check for swelling, tenderness, elbow stability, and overall movement. Imaging, such as X-rays or an MRI, may be ordered to rule out other types of elbow injuries, including ligament damage or fractures.
Non-operative treatment
Almost all elbow strains heal with conservative care, which may include:
- Resting the arm to avoid further strain
- Applying ice to reduce swelling
- NSAIDs to control pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy to restore strength and mobility once pain improves
A structured exercise program can help stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons around the elbow, supporting long-term recovery.
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely required for an elbow strain. However, in cases of severe injury or a complete muscle or tendon tear, surgery may be necessary to repair or reattach the damaged tissue.
Recovery
Most elbow strains heal within three to six weeks when treated promptly and properly. Athletes can safely return to sports once pain has resolved and the full range of motion and strength are restored. Following a gradual return-to-activity plan helps prevent reinjury.
Dr. Jay Kimmel is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon specializing in sports medicine, arthroscopic surgery, and shoulder and knee disorders. He completed his orthopedic training at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center and a Sports Medicine Fellowship at Temple University.
Dr. Kimmel previously served as the Director of the Connecticut Sports Medicine Institute at Saint Francis Hospital and has held faculty appointments as Clinical Assistant Professor in the Departments of Orthopedics and Family Medicine at the University of Connecticut. He has extensive experience caring for athletes as a team physician for high school and collegiate programs and continues to teach in the athletic training departments at Westfield State University and Springfield College.
Find the Support You Need — Right When You Need It
Whether you’re managing pain for the first time, need ongoing guidance, or require expert medical care, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
ORTHO DIRECT
Video visit with an orthopedic doctor for advice and a care plan.
$30
/MonthMRI DIRECT
Fast, affordable MRI with orthopedic review. No insurance required.
$499
/MonthFrequently Asked Questions
Can I treat a pulled elbow muscle at home?
Yes. Rest, ice, compression, and gentle stretching can help mild cases. If pain persists or worsens, see a doctor for proper elbow sprain treatment.
What's the typical recovery time for an elbow strain?
Most people recover within 3–6 weeks with conservative care and gradual return to activity.
What other conditions are often confused with an elbow strain?
Tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, bursitis, and elbow sprains can feel similar. A medical exam helps identify the exact injury.
Should I wear a brace for an overextended elbow?
A brace may help reduce strain and support healing, but it’s best to use one if your doctor or therapist recommends it.