Coccydynia refers to pain and inflammation at the tip of the coccyx. Also called the tailbone, the coccyx is located at the end of the spine and is one of the bones that make up the pelvis. Coccydynia causes pain and tenderness in between the buttocks in the area of the tailbone.
Coccydynia Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
Coccydynia refers to pain and inflammation at the tip of the coccyx. Also called the tailbone, the coccyx is located at the end of the spine and is one of the bones that make up the pelvis. Coccydynia causes pain and tenderness in between the buttocks in the area of the tailbone.
Overview
Overview
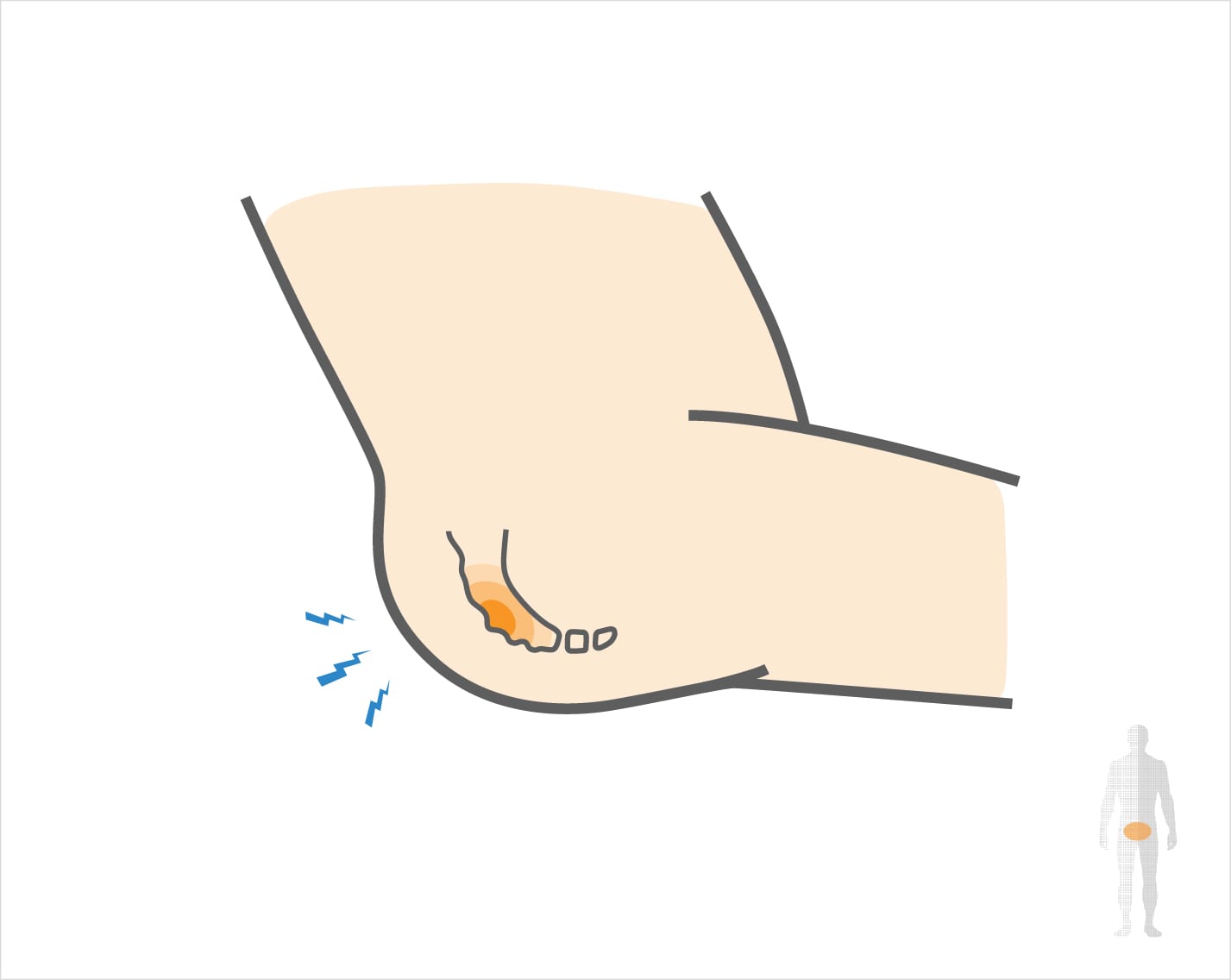
What causes Coccydynia?
A common cause of coccydynia is direct trauma to the tailbone, such as a fall. Chronic stress to the coccyx, through prolonged sitting or sports activity, can also lead to coccydynia. An unstable coccyx can cause chronic inflammation of the tailbone and lead to this condition. Often, no specific reason is identified for coccydynia, but it is a frequent cause of sitting pain and lower back discomfort in both active individuals and sedentary workers. In some cases, coccygeal pain may result from repetitive strain or posture-related issues.
Coccydynia is most common in these sports:
• Cycling
• Rowing
Symptoms
The major symptom associated with coccydynia is intense pain, especially when sitting. Common symptoms also include:
• Severe pain when standing up
• Pain gets better once standing or walking
• Deep ache in the tailbone
• Pain during bowel movements
When to see a doctor
If you have a painful tailbone, you should see your doctor, especially if your coccygeal pain persists for over a couple of days or if you’ve suffered an acute coccyx injury. Usually, your doctor can diagnose coccydynia by taking a medical history and physical examination so that you can get relief from tailbone pain. X-rays or other imaging tests may be ordered to determine if bone fractures or other conditions are causing your lower back discomfort or sitting pain.
Non-operative treatment
Pain resulting from coccydynia often resolves on its own over time, though it may take several weeks. Treatment usually involves rest and abstaining from activities such as sports and prolonged sitting that can aggravate the tailbone. Conservative treatments also include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, to relieve pain
- Corticosteroid (anti-inflammatory medicine) injections can heal and give relief from tailbone pain
- Using a special, wedge-shaped cushion that shifts weight off the tailbone when sitting to reduce pain
- Physical therapy exercises to strengthen muscles that support the lower back
Try these exercises to help address your condition:
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Surgical Treatment
In rare cases, when conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be recommended to remove part of the coccyx.
Recovery
It’s essential to give your tailbone time to recover so that you can experience relief from tailbone pain. It may take several weeks to be fully pain-free and return to regular activity. Pushing yourself too soon with very strenuous activity could delay your recovery. Your doctor may advise that you start with light exercise before a full return to play.
GET BACK TO WHAT YOU LOVE. FASTER
Sources
https://www.medicinenet.com/coccydynia/article.htm
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10436-coccydynia-tailbone-pain
https://runnerclick.com/coccyx-tailbone-injury/
https://www.orthoinfo.org/en/diseases–conditions/pelvic-fractures/
https://www.livestrong.com/article/461351-can-i-exercise-after-a-coccyx-fracture/
Frequently Asked Questions
How is coccydynia different from general lower back pain?
While both involve lower back discomfort, coccydynia specifically centers on the coccyx or tailbone, and the pain is often worse when sitting or leaning back.
What treatment options are available for coccydynia?
Treatment often begins with conservative measures like using a cushion, applying ice or heat, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. For persistent coccygeal pain, steroid injections or, in very rare cases, surgical removal of the coccyx may be considered.
How long does it take to recover from a coccyx injury?
Recovery time can vary. Mild coccyx injuries or strains may heal in a few weeks, while chronic coccydynia can take several months to resolve.
Can coccydynia become a long-term condition?
Yes, if left untreated, coccydynia can become chronic and significantly affect daily activities by causing constant sitting pain and lower back discomfort. Early diagnosis and proper management improve the chances of full recovery.