The distal biceps tendon, which connects the biceps muscle to the elbow bone, can become inflamed and weakened due to overuse. This condition, called tendonitis, can cause pain and limited movement.
Distal Biceps Tendonitis Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
The distal biceps tendon, which connects the biceps muscle to the elbow bone, can become inflamed and weakened due to overuse. This condition, called distal biceps tendonitis, can cause pain and limited movement, especially around the elbow joint.
Overview
Overview
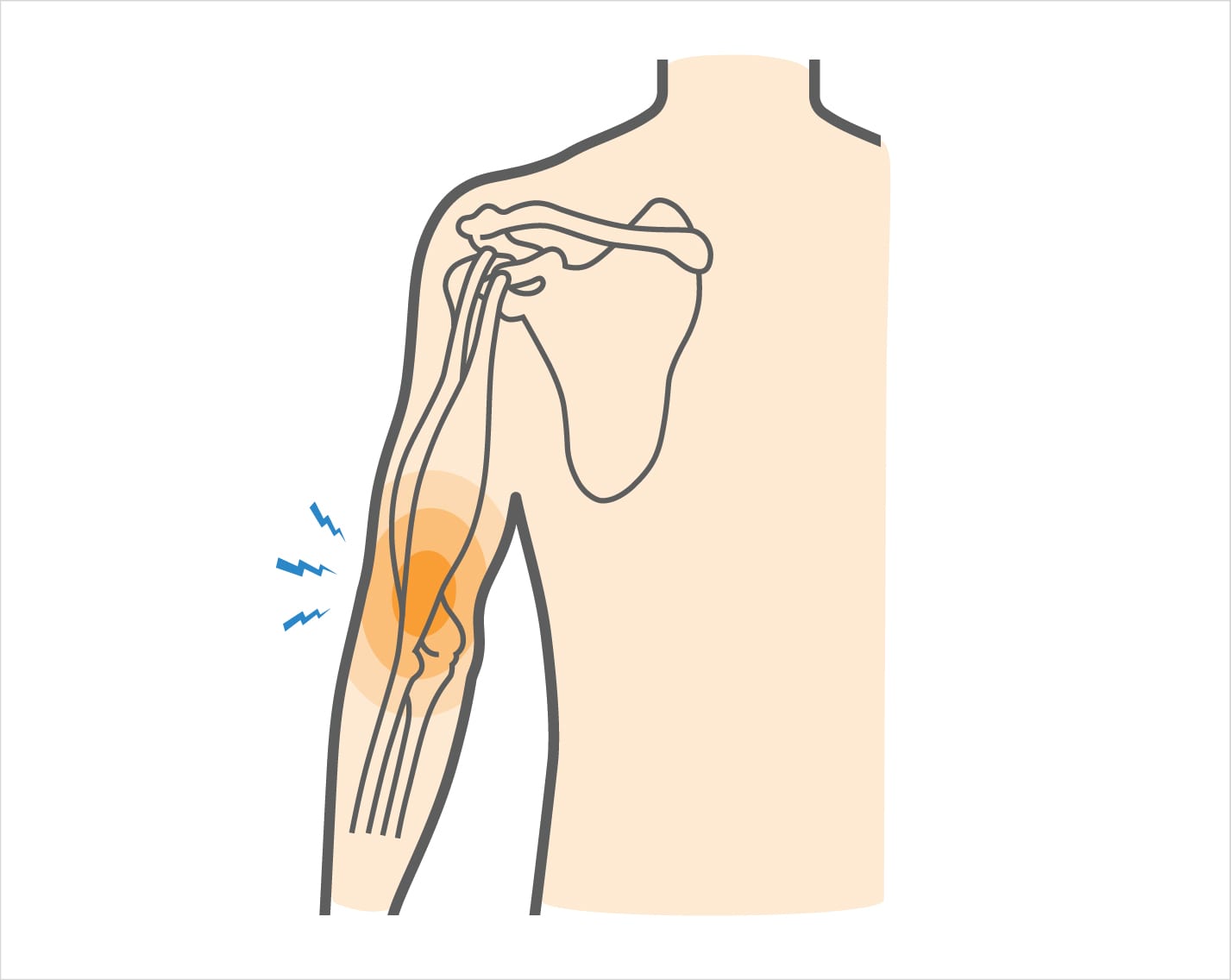
What causes Distal Biceps Tendonitis?
Distal biceps tendonitis is typically caused by overuse or repetitive activities that place strain on the biceps tendon. This biceps strain is common in sports and occupations that involve repetitive pulling or lifting motions.
Repetitive lifting injuries are a frequent cause, especially when the arm is bent and weight is improperly lifted.
Biceps tendonitis is common in these sports:
- Weightlifting
- Bodybuilding
- Gymnastics
- Bowling
- Baseball
- Softball
- Tennis
- Golf
Symptoms
Common symptoms you may experience if you have distal biceps tendonitis include:
- Pain in the front of the elbow while throwing, working out, or playing your sport
- Stiffness and soreness on the front of the bicep near the elbow
- Tenderness or minor swelling over the biceps tendon
- Dull pain that worsens when bending the arm against resistance or twisting the arm, like when using a screwdriver or opening a jar
When to see a doctor
If you experience these symptoms, you should see your doctor, who will take a medical history and conduct a physical exam. He or she may also prescribe an X-ray to rule out other injuries or an MRI to make sure you don’t have a ruptured tendon or another problem.
Non-operative treatment
Distal biceps tendonitis is almost always treated without surgery. Initial treatment typically involves rest and avoiding activities that worsen the biceps strain. Ice applied for 10 minutes every hour during the first couple of days may help reduce inflammation.
Your doctor may also prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like aspirin or ibuprofen, to relieve pain and decrease lower biceps tendon inflammation. Physical therapy is commonly recommended to restore flexibility and strength.
Try these exercises to help address your condition:
Below is a PDF of the Exercise Program
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually not necessary for distal biceps tendonitis unless the tendon in the elbow is ruptured. This is rare but may be considered if there is complete tearing or severe loss of function.
Recovery
Almost always, distal biceps tendonitis is treated successfully with non-operative methods. If the recommended treatment is followed, full recovery can usually be expected within six to eight weeks.
Athletes should take care to prevent further injury by warming up properly before activity and using ice on the elbow if elbow front pain recurs after exertion.
GET BACK TO WHAT YOU LOVE. FASTER
Sources
https://www.physioadvisor.com.au/injuries/elbow-forearm/biceps-tendonitis/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/biceps-tendon-tear-at-the-elbow/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tendinitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378243
http://www.assh.org/handcare/hand-arm-injuries/Distal-Biceps-Tendon-Problems
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical treatment timeline for recovery?
With conservative treatment, most patients recover from distal biceps tendonitis within 3 to 6 weeks. Severe or chronic cases may take longer, especially if the individual continues activities that aggravate the injury.
What types of activities should be avoided during recovery?
Avoid repetitive lifting, pulling, or twisting motions that cause pain, especially overhead lifting. These can worsen a biceps strain and prolong healing.
Do I really need physical therapy to get better?
Physical therapy plays a critical role in reducing lower biceps tendon inflammation, restoring the full range of motion, and preventing future injuries.
Can distal biceps tendonitis become a chronic condition?
Yes. If left untreated or if activity is resumed too early after a lifting injury, the tendon can remain inflamed, leading to long-term discomfort and reduced arm function.